Telegraphs
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of textual or symbolic (as opposed to verbal or audio) messages without the physical exchange of an object bearing the message.
Telegraphy requires that the method used for encoding the message be known to both sender and receiver. Such methods are designed according to the limits of the signalling medium used.
The use of smoke signals, beacons, reflected light signals, and flag semaphore signals are early examples. In the 19th century, the harnessing of electricity led to the invention of electrical telegraphy.
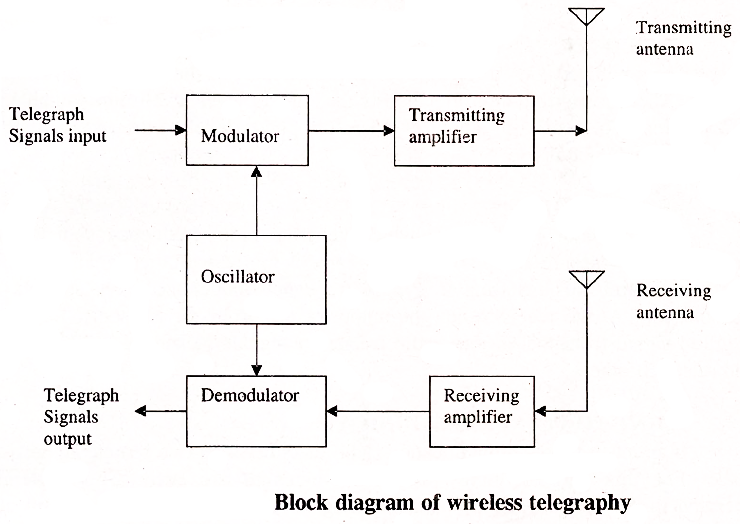
The advent of radio in the early 20th century brought about radiotelegraphy and other forms of wireless telegraphy.
In the Internet age, telegraphic means developed greatly in sophistication and ease of use, with natural language interfaces that hide the underlying code, allowing such technologies as electronic mail and instant messaging.
The word "telegraph" was first coined by the French inventor of the Semaphore line, Claude Chappe, who also coined the word "semaphore".
A "telegraph" is a device for transmitting and receiving messages over long distances, i.e., for telegraphy. The word "telegraph" alone now generally refers to an electrical telegraph.
A telegraph message sent by an electrical telegraph operator or telegrapher using Morse code (or a printing telegraph operator using plain text) was known as a telegram.
`text(How It Works)`
The operator at the sending station pushes down an operator key that closes the electronic circuit and sends a signal through the telegraph lines or wires to the receiver.
When the signal reaches the receiver, it activates a magnet that pulls down the key at the receiver station completing the circuit. Pushing and then releasing the key on the sender’s side allows current to flow or be interrupted in pulses.
This series of pulses is called Morse Code. Morse Code assigns a specific pattern of dots and dashes to letters of the alphabet.
The most easily recognized example of Morse Code is dot-dot-dot, dash-dash-dash, dot-dot-dot, or SOS.
Telegraphy requires that the method used for encoding the message be known to both sender and receiver. Such methods are designed according to the limits of the signalling medium used.
The use of smoke signals, beacons, reflected light signals, and flag semaphore signals are early examples. In the 19th century, the harnessing of electricity led to the invention of electrical telegraphy.
The advent of radio in the early 20th century brought about radiotelegraphy and other forms of wireless telegraphy.
In the Internet age, telegraphic means developed greatly in sophistication and ease of use, with natural language interfaces that hide the underlying code, allowing such technologies as electronic mail and instant messaging.
The word "telegraph" was first coined by the French inventor of the Semaphore line, Claude Chappe, who also coined the word "semaphore".
A "telegraph" is a device for transmitting and receiving messages over long distances, i.e., for telegraphy. The word "telegraph" alone now generally refers to an electrical telegraph.
A telegraph message sent by an electrical telegraph operator or telegrapher using Morse code (or a printing telegraph operator using plain text) was known as a telegram.
`text(How It Works)`
The operator at the sending station pushes down an operator key that closes the electronic circuit and sends a signal through the telegraph lines or wires to the receiver.
When the signal reaches the receiver, it activates a magnet that pulls down the key at the receiver station completing the circuit. Pushing and then releasing the key on the sender’s side allows current to flow or be interrupted in pulses.
This series of pulses is called Morse Code. Morse Code assigns a specific pattern of dots and dashes to letters of the alphabet.
The most easily recognized example of Morse Code is dot-dot-dot, dash-dash-dash, dot-dot-dot, or SOS.