Properties Of Triangles
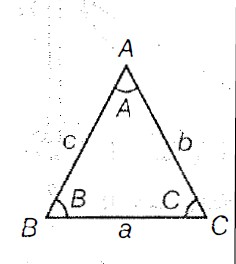
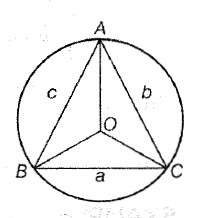
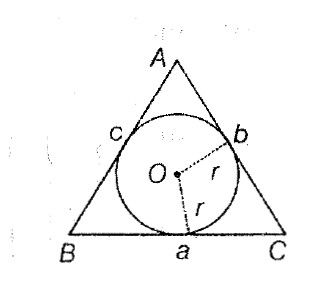
A triangle has six components, three sides and three angles. The three angles of a `triangle ABC` are denoted by the letters A, B and C and the sides opposite to these angles by letters `a, b` and `c` respectively, i.e. `a= BC, b = CA` and `c = AB`. Semi-perimeter of the
`triangle ABC` is `(a+b+c)/2` which is denoted by `s` and its area denoted by `Delta`
Also, sum of angles of a triangle is `180°`, i.e. `angle A + angle B + angle C = 180°`
`triangle ABC` is `(a+b+c)/2` which is denoted by `s` and its area denoted by `Delta`
Also, sum of angles of a triangle is `180°`, i.e. `angle A + angle B + angle C = 180°`