Introduction :
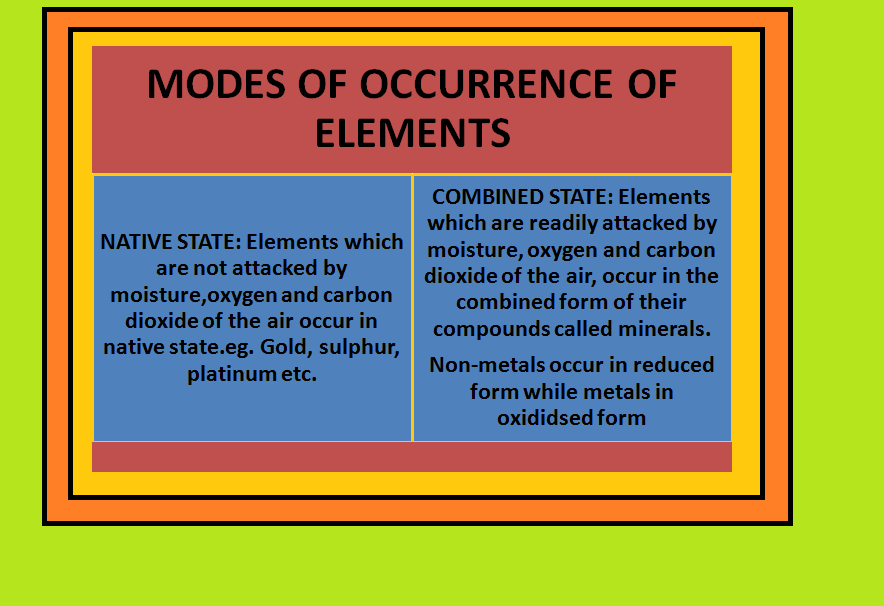
`=>` A few elements like carbon, sulphur, gold and noble gases occur in free state while others in combined forms in the earth’s crust.
`=>` The extraction and isolation of an element from its combined form involves various principles of chemistry.
`=>` A particular element may occur in a variety of compounds.
`=>` The process of metallurgy and isolation should be such that it is chemically feasible and commercially viable.
`=>` Some general principles are common to all the extraction processes of metals.
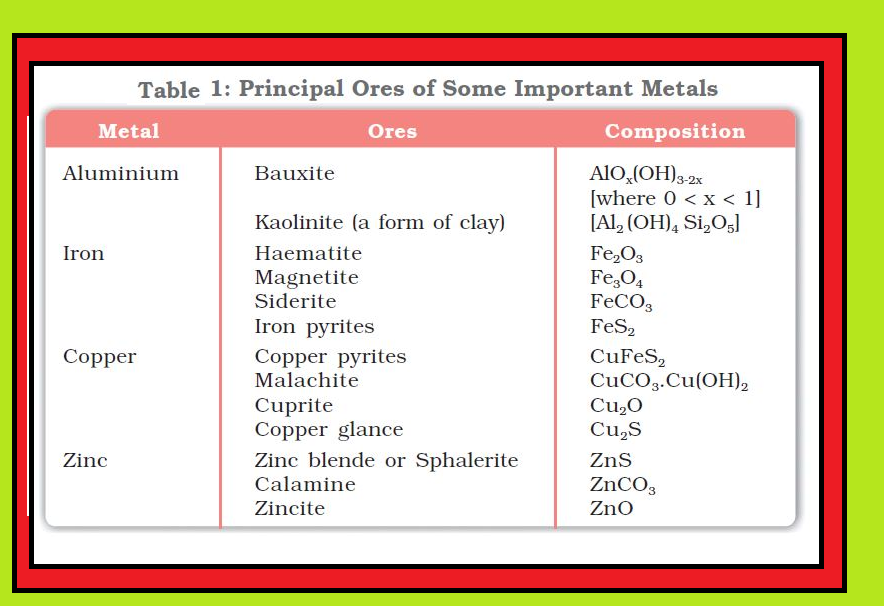
`text(Minerals :)` These are naturally occurring chemical substances in the earth’s crust obtainable by mining.
`text(Ores :)` Minerals in which a metal may be found, only a few are viable to be used as sources of that metal. Such minerals are known as ores.
`=>` Rarely, an ore contains only a desired substance. It is usually contaminated with earthly or undesired materials known as `text(gangue)`.
`=>` The extraction and isolation of metals from ores involve the following major steps :
• Concentration of the ore
• Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore and
• Purification of the metal.
`text(Metallurgy :)` The entire scientific and technological process used for isolation of the metal from its ores is known as metallurgy.
`=>` The extraction and isolation of an element from its combined form involves various principles of chemistry.
`=>` A particular element may occur in a variety of compounds.
`=>` The process of metallurgy and isolation should be such that it is chemically feasible and commercially viable.
`=>` Some general principles are common to all the extraction processes of metals.
`text(Minerals :)` These are naturally occurring chemical substances in the earth’s crust obtainable by mining.
`text(Ores :)` Minerals in which a metal may be found, only a few are viable to be used as sources of that metal. Such minerals are known as ores.
`=>` Rarely, an ore contains only a desired substance. It is usually contaminated with earthly or undesired materials known as `text(gangue)`.
`=>` The extraction and isolation of metals from ores involve the following major steps :
• Concentration of the ore
• Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore and
• Purification of the metal.
`text(Metallurgy :)` The entire scientific and technological process used for isolation of the metal from its ores is known as metallurgy.