Reduction of nitro compounds :
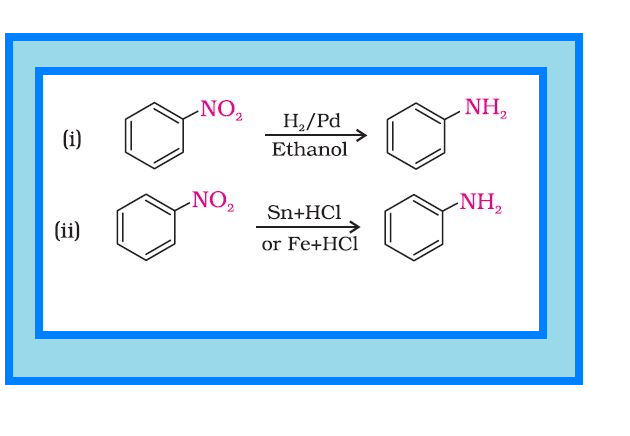
`=>` Nitro compounds are reduced to amines by passing hydrogen gas in the presence of finely divided nickel, palladium or platinum and also by reduction with metals in acidic medium.
`=>` Nitroalkanes can also be similarly reduced to the corresponding alkanamines.
`=>` Reduction with iron scrap and hydrochloric acid is preferred because `color{red}(FeCl_2)` formed gets hydrolysed to release hydrochloric acid during the reaction. Thus, only a small amount of hydrochloric acid is required to initiate the reaction.
`=>` Nitroalkanes can also be similarly reduced to the corresponding alkanamines.
`=>` Reduction with iron scrap and hydrochloric acid is preferred because `color{red}(FeCl_2)` formed gets hydrolysed to release hydrochloric acid during the reaction. Thus, only a small amount of hydrochloric acid is required to initiate the reaction.