Electrochemical Cell
A cell in which spontaneous redox reaction is carried out to produce an electric current is called electrochemical cell.
`=>` An electrochemical cell comprises of two metallic electrodes namely anode [-ve electrode] and cathode [+ve electrode] dipped in electrolytic solution.
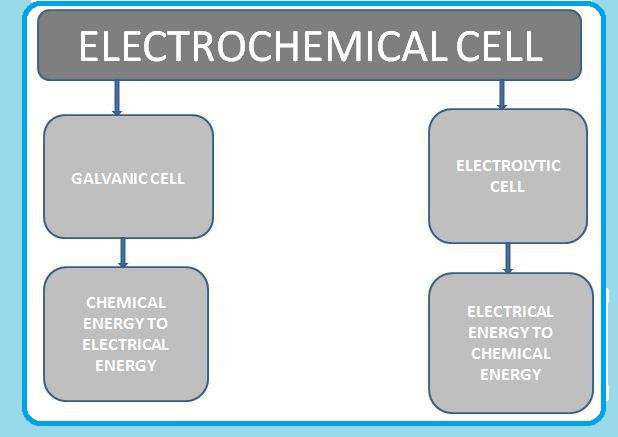
`=>` There are two types of electrochemical cell galvanic cell and electrolytic cell.
`=>` In galvanic cell, the chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction is converted into electrical energy.
`=>` In electrolytic cells, electrical energy is used to carry out a non-spontaneous reaction.
`=>` An electrochemical cell comprises of two metallic electrodes namely anode [-ve electrode] and cathode [+ve electrode] dipped in electrolytic solution.
`=>` There are two types of electrochemical cell galvanic cell and electrolytic cell.
`=>` In galvanic cell, the chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction is converted into electrical energy.
`=>` In electrolytic cells, electrical energy is used to carry out a non-spontaneous reaction.
