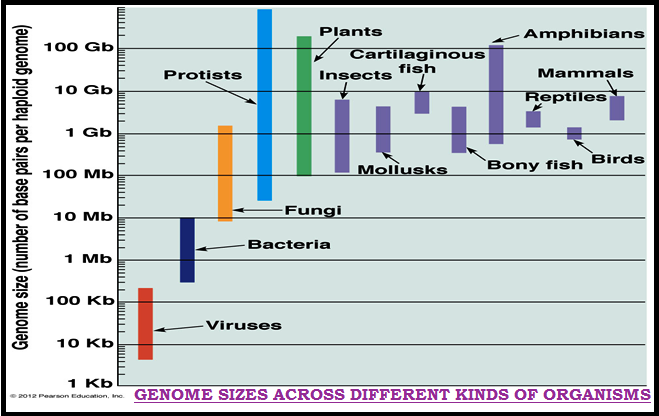
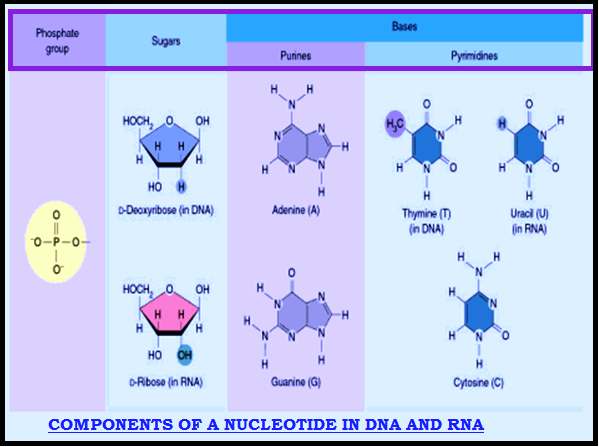
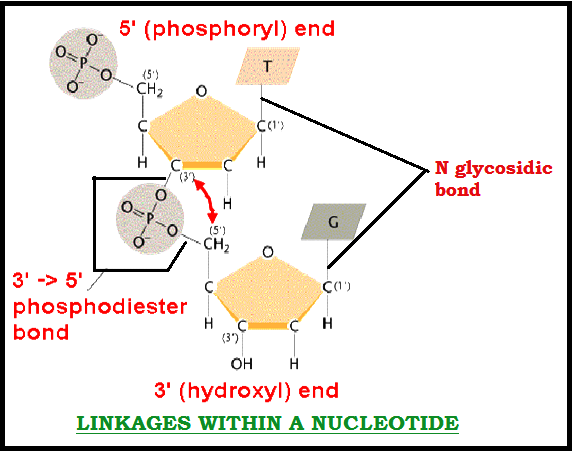
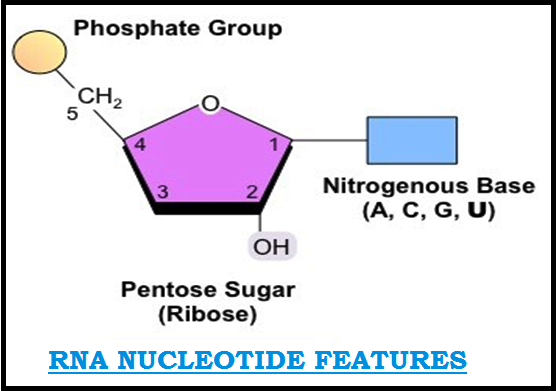
INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEIC ACIDS
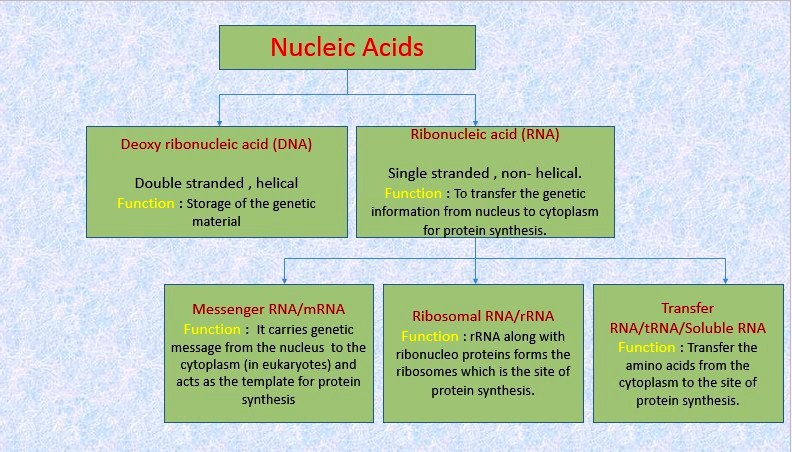
● `color{Violet}"Deoxyribonucleic acid"` (DNA) and `color{Violet}"ribonucleic acid"` (RNA) are the two types of nucleic acids found in living systems.
● `color{brown}"Role of DNA"`:
`star` DNA acts as the `color{Violet}"genetic material"` in most of the organisms.
● `color{brown}"Role of RNA"`:
`star` `color{Violet}"RNA"` though it also acts as a genetic material in some `color{Violet}"viruses"`, mostly functions as a `color{Violet}"messenger"`.
`star` RNA has additional roles as well. It functions as `color{Violet}"adapter"`, `color{Violet}"structural"`, and in some cases as a `color{Violet}"catalytic molecule"`.
● `color{brown}"Role of DNA"`:
`star` DNA acts as the `color{Violet}"genetic material"` in most of the organisms.
● `color{brown}"Role of RNA"`:
`star` `color{Violet}"RNA"` though it also acts as a genetic material in some `color{Violet}"viruses"`, mostly functions as a `color{Violet}"messenger"`.
`star` RNA has additional roles as well. It functions as `color{Violet}"adapter"`, `color{Violet}"structural"`, and in some cases as a `color{Violet}"catalytic molecule"`.