ETHICAL ISSUES REGARDING GMOs
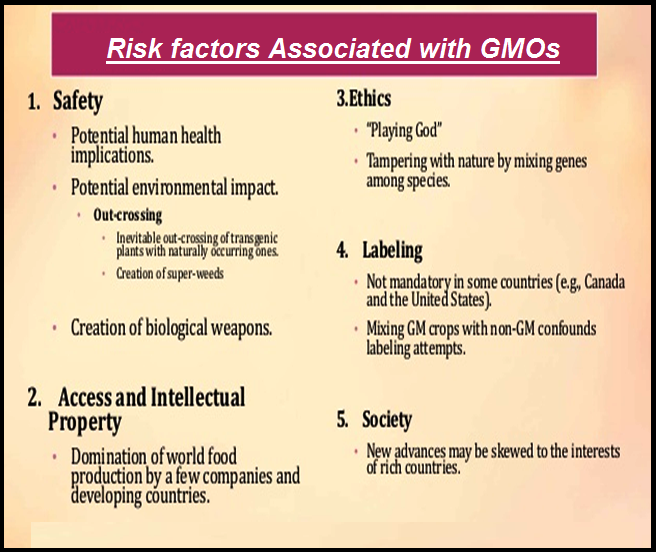
● The `color{violet}("manipulation of living organisms")` by the human race cannot go on any further, `color{violet}("without regulation")`.
● Some ethical standards are required to evaluate the `color{violet}("morality")` of all human activities that might help or `color{violet}("harm living organisms")`.
● Going beyond the `color{violet}("morality")` of such issues, the `color{violet}("biological significance")` of such things is also important.
● `color{violet}("Genetic modification of organisms")` can have unpredicatable results when such `color{violet}("organisms")` are introduced into the `color{violet}("ecosystem")`.
● Therefore, the Indian Government has set up organisations such as `color{violet}("GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee)")`, which will make decisions regarding the validity of GM research and the safety of introducing `color{violet}("GM-organisms")` for public services.
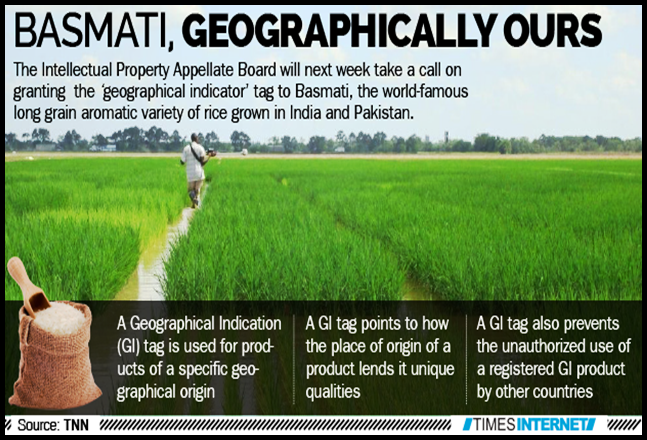
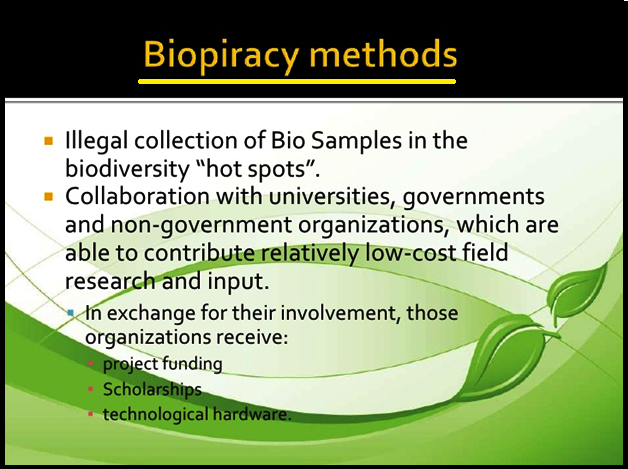
● The `color{violet}("modification/usage of living organisms")` for public services (as `color{violet}("food ")`and `color{violet}("medicine")` sources, for example) has also created problems with patents granted for the same.
● Some ethical standards are required to evaluate the `color{violet}("morality")` of all human activities that might help or `color{violet}("harm living organisms")`.
● Going beyond the `color{violet}("morality")` of such issues, the `color{violet}("biological significance")` of such things is also important.
● `color{violet}("Genetic modification of organisms")` can have unpredicatable results when such `color{violet}("organisms")` are introduced into the `color{violet}("ecosystem")`.
● Therefore, the Indian Government has set up organisations such as `color{violet}("GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee)")`, which will make decisions regarding the validity of GM research and the safety of introducing `color{violet}("GM-organisms")` for public services.
● The `color{violet}("modification/usage of living organisms")` for public services (as `color{violet}("food ")`and `color{violet}("medicine")` sources, for example) has also created problems with patents granted for the same.