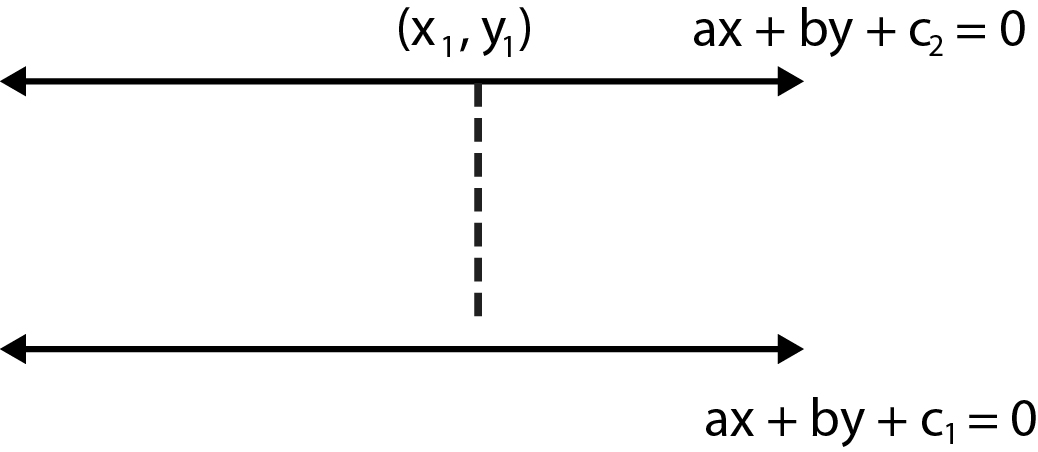
Length of the Perpendicular :
The length of the perpendicular from a point `(x_1, y_1)` to a line `ax + by+ c = 0` is
`|(ax_1+by_1+c)/(sqrt(a^2+b^2)|`
Proof :
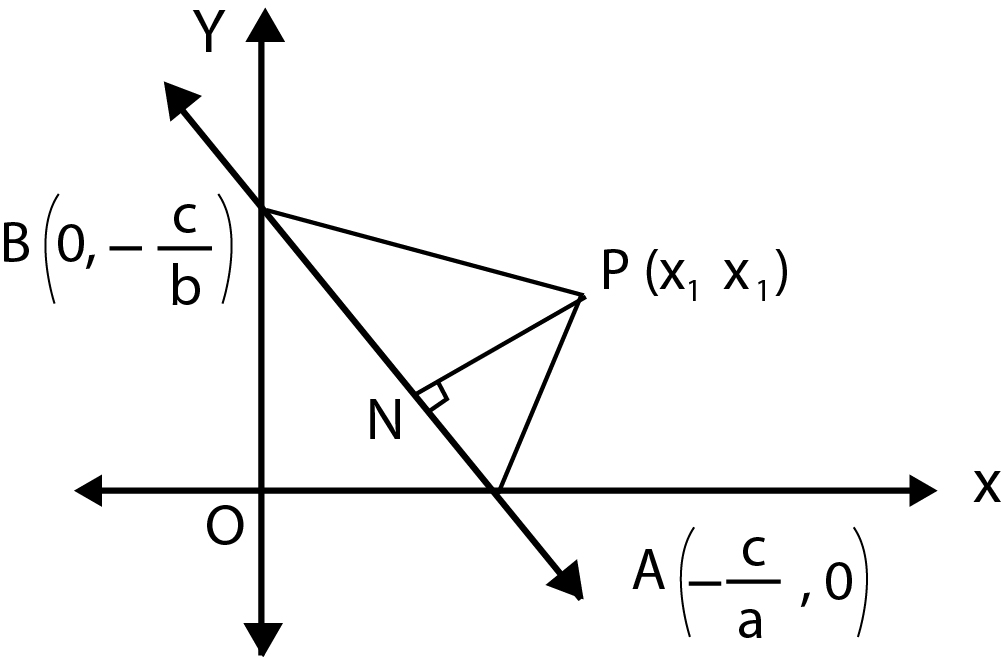
The line `ax + by + c = 0` meets `x`-axis at `A(-c/a,0)` and `y`-axis at `B(0,-c/b)`
Let `P(x_1, y_1)` be the point. Draw `PN bot AB`.
Now, area of `Delta PAB`
`1/2|x_1(0+c/b)-c/a(-c/b-y_1)+0(y_1-0)|`
`1/2|(cx_1)/b+(cy_1)/a+c^2/(ab)|=|(ax_1+by_1+c)c/(2ab)|`.......................(i)
Also, area of `Delta PAB`
`=1/2 AB xx PN`
`=1/2sqrt(c^2/a^2+c^2/b^2) xx PN`
`= c/(2ab)sqrt(a^2+b^2) xx PN`....................(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
`|(ax_1+by_1+c)c/(2ab)|=c/(2ab) sqrt(a^2+b^2)xx PN`
`=> PN=(|ax_1+by_1+c|)/(sqrt(a^2+b^2))`
`|(ax_1+by_1+c)/(sqrt(a^2+b^2)|`
Proof :
The line `ax + by + c = 0` meets `x`-axis at `A(-c/a,0)` and `y`-axis at `B(0,-c/b)`
Let `P(x_1, y_1)` be the point. Draw `PN bot AB`.
Now, area of `Delta PAB`
`1/2|x_1(0+c/b)-c/a(-c/b-y_1)+0(y_1-0)|`
`1/2|(cx_1)/b+(cy_1)/a+c^2/(ab)|=|(ax_1+by_1+c)c/(2ab)|`.......................(i)
Also, area of `Delta PAB`
`=1/2 AB xx PN`
`=1/2sqrt(c^2/a^2+c^2/b^2) xx PN`
`= c/(2ab)sqrt(a^2+b^2) xx PN`....................(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
`|(ax_1+by_1+c)c/(2ab)|=c/(2ab) sqrt(a^2+b^2)xx PN`
`=> PN=(|ax_1+by_1+c|)/(sqrt(a^2+b^2))`