Addition Theorem On Probability :
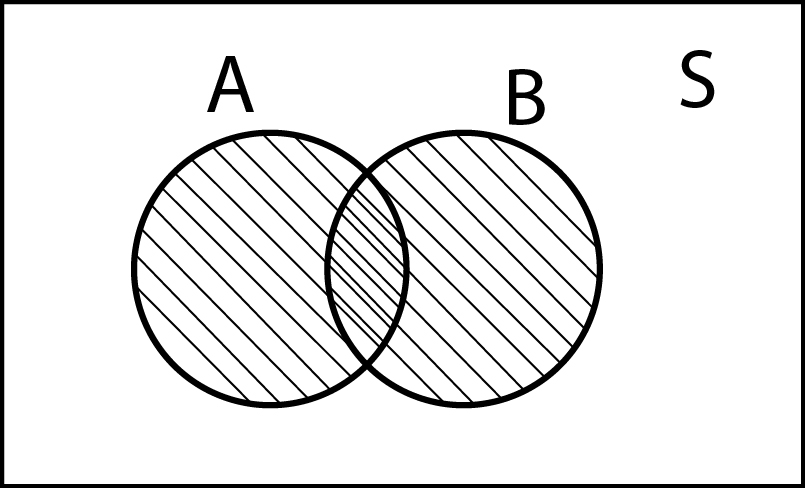
If `A` and `B` are two events associated with an experiment then `P(A cup B)` is called the sum of the probabilities of all the sample points in `A cup B` or probability of occurrence of atleast one of the events from `A` and `B` and the expression for `P(A cup B)` is called the addition theorem on probability From the Venn diagram it is clear that
`P`(Occurence at least one of the events from `A` and `B`) `P`(`A` or `B` or both) or `P(A + B)`
`=>P(A cup B)=P(A)+P(B)-P(A cap B)`
`=P(A)+P(bar A cap bar B)`
`=P(B)+(A cap bar B)`
`=P(A cap bar B)+P(AB)+P(bar A cap B)`
`=1-P(bar A cap B)`
`=1-P(bar(A cap B))`
`text(Note :)`
(i) If A and Bare mutually exclusive events then
`p(AuuB) = p(A) + p(B)` `\ \ \ \ {because p(AnnB) = 0`}
(ii) If A and Bare exhaustive events then `P(A uu B) = 1`
(iii) `P(A uu B) = 1 - bar(P(A uu B))`
`P`(Occurence at least one of the events from `A` and `B`) `P`(`A` or `B` or both) or `P(A + B)`
`=>P(A cup B)=P(A)+P(B)-P(A cap B)`
`=P(A)+P(bar A cap bar B)`
`=P(B)+(A cap bar B)`
`=P(A cap bar B)+P(AB)+P(bar A cap B)`
`=1-P(bar A cap B)`
`=1-P(bar(A cap B))`
`text(Note :)`
(i) If A and Bare mutually exclusive events then
`p(AuuB) = p(A) + p(B)` `\ \ \ \ {because p(AnnB) = 0`}
(ii) If A and Bare exhaustive events then `P(A uu B) = 1`
(iii) `P(A uu B) = 1 - bar(P(A uu B))`
