`(i) 1 + omega + omega^2 = 0` and `omega^3=1`
`(ii)` `omega^(3n) = 1 , omega^(3m + 1) + omega , omega^(3n + 2) = omega^2`
`(iii) 1 + omega^r + omega^(2r) =` `{tt[(3,text{when n is a multiple of 3}),(0, text{when n. is not a multiple of 3})]`
`(iv)` Cube roots of- 1 are- 1,- `omega` and- `omega^2`
`(v)` `a + b omega + c omega^2 = 0`
`=> a = b = c ,` if `a,b,c in R`
`(vi)` If `a, b, c` are non-zero numbers such that `a+ b + c = 0 = a^2 + b^2 + c^2` , then `a : b : c = 1 : omega : omega^2`
.
`(vii)` A complex number `a+ ib` (where `i = sqrt(-1),` for which `|a : b| = 1 : sqrt3` or `sqrt3 : 1` can always be expressed in terms of `omega` or `omega^2`
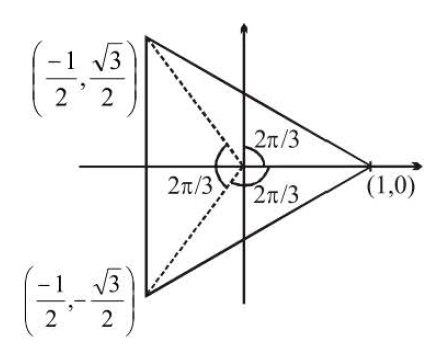
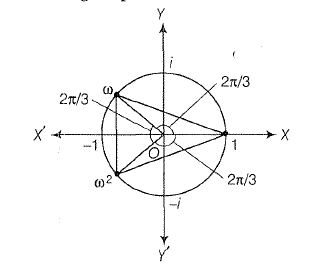
`(viii)` The cube roots of unity when represented on complex plane lie on
vertices of an equilateral triangle inscribed in a unit circle, having centre
at origin. One vertex being on positive real axis.
`text(Important Relations)`
`(i) a^2 + ab + b^2 = (a-bomega)(a- bomega^2)`
`(ii) a^2 - ab +b^2 + (a+bomega)(a+bomega^2)`
`(iii) a^3 + b^3 = (a+b)(a+b omega)(a+ b omega^2)`
`(iv) a^3-b^3 = (a-b)(a+ bomega)(a-bomega^2)`
`(v) a^2+b^2+c^2-ab - bc -ca = (a+ b omega + c omega^2)(a + b omega^2 + c omega)`
`(vi) a^3 + b^3 + c^3 - 3abc = (a+b+c) (a+b omega + c omega^2)(a + b omega + c omega)`
`(i) 1 + omega + omega^2 = 0` and `omega^3=1`
`(ii)` `omega^(3n) = 1 , omega^(3m + 1) + omega , omega^(3n + 2) = omega^2`
`(iii) 1 + omega^r + omega^(2r) =` `{tt[(3,text{when n is a multiple of 3}),(0, text{when n. is not a multiple of 3})]`
`(iv)` Cube roots of- 1 are- 1,- `omega` and- `omega^2`
`(v)` `a + b omega + c omega^2 = 0`
`=> a = b = c ,` if `a,b,c in R`
`(vi)` If `a, b, c` are non-zero numbers such that `a+ b + c = 0 = a^2 + b^2 + c^2` , then `a : b : c = 1 : omega : omega^2`
.
`(vii)` A complex number `a+ ib` (where `i = sqrt(-1),` for which `|a : b| = 1 : sqrt3` or `sqrt3 : 1` can always be expressed in terms of `omega` or `omega^2`
`(viii)` The cube roots of unity when represented on complex plane lie on
vertices of an equilateral triangle inscribed in a unit circle, having centre
at origin. One vertex being on positive real axis.
`text(Important Relations)`
`(i) a^2 + ab + b^2 = (a-bomega)(a- bomega^2)`
`(ii) a^2 - ab +b^2 + (a+bomega)(a+bomega^2)`
`(iii) a^3 + b^3 = (a+b)(a+b omega)(a+ b omega^2)`
`(iv) a^3-b^3 = (a-b)(a+ bomega)(a-bomega^2)`
`(v) a^2+b^2+c^2-ab - bc -ca = (a+ b omega + c omega^2)(a + b omega^2 + c omega)`
`(vi) a^3 + b^3 + c^3 - 3abc = (a+b+c) (a+b omega + c omega^2)(a + b omega + c omega)`