Weightlessness in a Satellite :
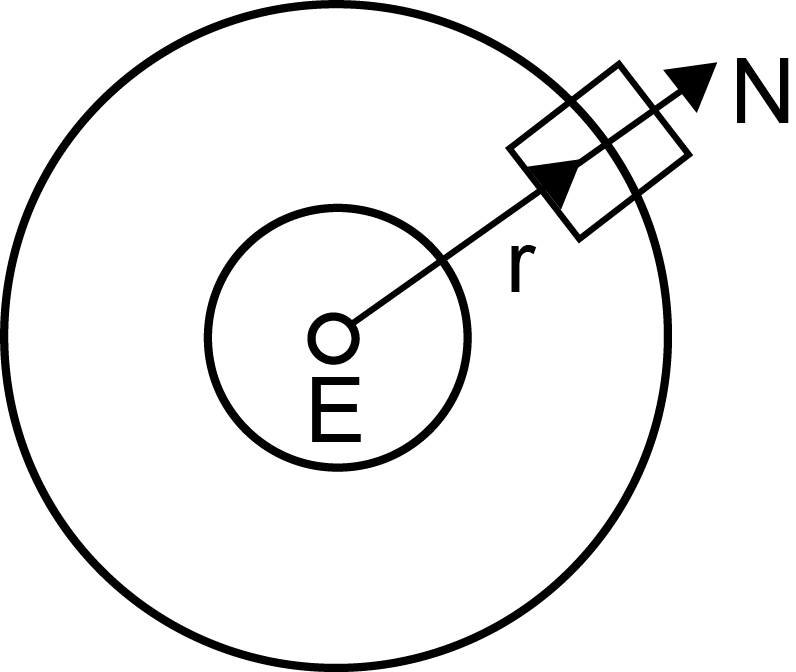
The radial acceleration of the satellite is given by `a_r = F_r/m = (GMm)/(r^2 xx m) = (GM)/r^2`
For an astronaut inside the satellite, we have
`(GMm_a)/r^2-N-m_a a_r=0`
where m , is mass of astronaut a , is radial acceleration of
satellite and N is normal reaction on the astronaut
`(GMm_a)/r^2-N-(GMm_a)/r^2=0=> N=0`
Hence, the astronaut feels weightlessness.
For an astronaut inside the satellite, we have
`(GMm_a)/r^2-N-m_a a_r=0`
where m , is mass of astronaut a , is radial acceleration of
satellite and N is normal reaction on the astronaut
`(GMm_a)/r^2-N-(GMm_a)/r^2=0=> N=0`
Hence, the astronaut feels weightlessness.