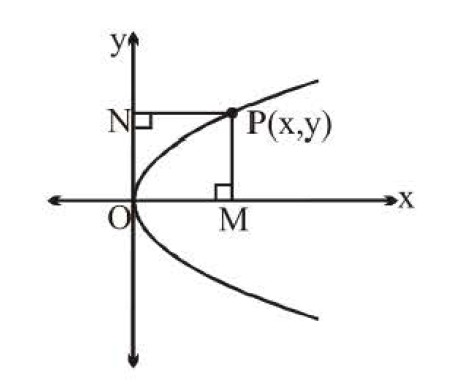
lf the equation of a parabola is either in the form `x =l y^2 + my + n` or `y = l x^2+ mx + n` then it can be reduced into generalised form. For this we change the given equation into the following forms-
`(y - k)^2 = 4a (x - h)` or `(x - h)^2 = 4a (y - k)`
And then we compare from the standard equation of parabola to find all its parameters.
(A) When the equation of parabola is : `(y -k)^2 = 4a(x - h)`
`(y -k)^2 = 4a(x - h)`................(i)
Equation (i) is of the form `Y^2 = 4aX`
where `Y = y - k` and `X = x - h`
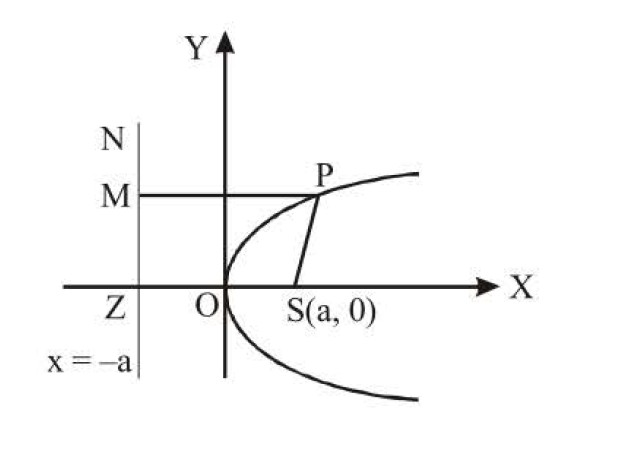
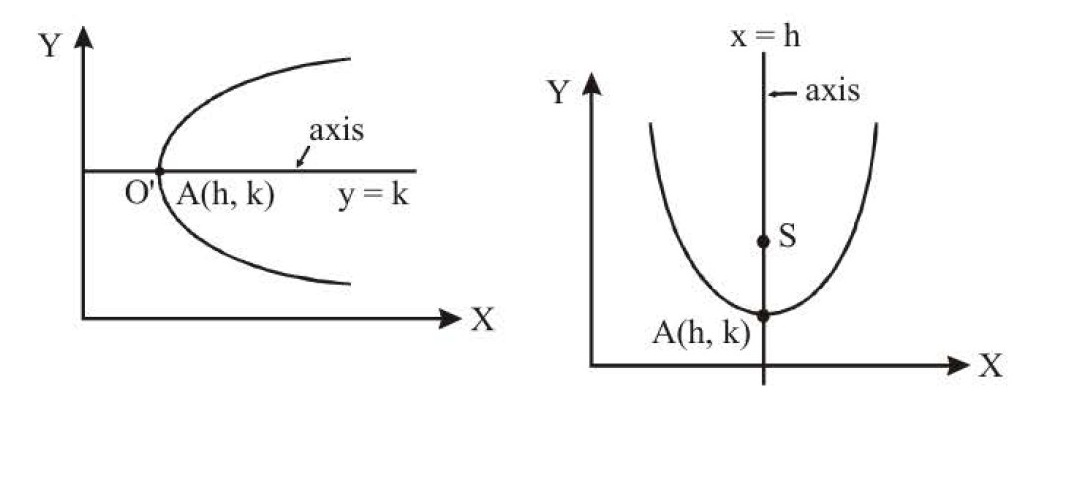
(1) Axis of parabola is `Y = 0`, i.e., ` y - k = 0 => y = k`
(2) Coordinates of vertex of parabola are given by
`X=0` and `Y=0`
i.e, `x-h=0` and `y-k=0`
`:.` Vertex is `(h,k)`
(3) Tangent at the vertex to parabola (i) is given by
`X=0`, i. e. , `x - h = 0`
Therefore, tangent at the vertex is `x = h` .
(4) Coordinates of focus of parabola are given by
`X = a` and `Y = 0`
i.e. by `x - h = a` and `y - k = 0`
`:.` Focus of parabola is `(a + h, k)`.
(5) Equation of directrix of parabola is
`X =-a`
i.e., `x - h = -a`
Therefore, directrix of parabola is `x = h - a`
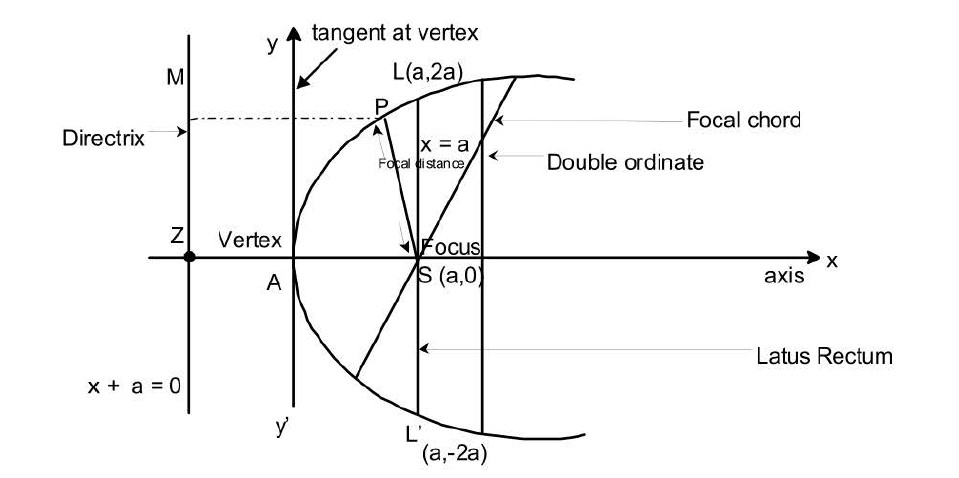
(6) Length of latus rectum of parabola is `|4a |`
(7) Coordinates of ends of latus rectum of parabola are given by
`X=a` & `Y=+-2a`
i.e., by `x-h=a` , `y-k=+-2a`
i.e., coordinate of latus rectum is `(a+h,k+-2a)`.
(8) Parametric equation is `x = h + at^2` and `y = k + 2at`.
(B) When the equation of parabola is :
`(x - h)^2 = 4a (y - k)` ........................(i)
Equation (i) is of the form `X^2 = 4aY`
where `X = x - h` and `Y = y - k`
(1) Axis of parabola is `X = 0`, i.e. , `x - h = 0`
(2) Coordinates of vertex of parabola is given by
`X = 0` and `Y = 0`
i.e. , by `x - h = 0` and `y - k = 0`
`:. x=h` and `y=k`
Hence vertex of parabola is `(h , k)`
(3) Equation of tangent at the vertex to parabola is
`Y = 0` i.e. , `y - k = 0`
or `y = k`
(4) Coordinates of focus of parabola are given by
`X=0` and `Y=a`
i.e., by `x-h=0` and `y-k=a`
`:.` Focus of Parabola is `(h,k+a)`.
(5) Equation of directrix of parabola (i) is given by
`Y =-a` or `y - k = - a` or `y = k - a`
(6) Length of latus rectum of parabola is `|4a |`.
(7) Coordinates of ends of latus rectum of parabola are given by
`Y=a` , `X=+-2a`
i.e., `y-k=a` , `X-h =+-2a`
`:.` Ends of latus ractum are `(h+-2a,k+a)`
(8) Parametric equation is `x=h+2at` and `y=k+at^2`
lf the equation of a parabola is either in the form `x =l y^2 + my + n` or `y = l x^2+ mx + n` then it can be reduced into generalised form. For this we change the given equation into the following forms-
`(y - k)^2 = 4a (x - h)` or `(x - h)^2 = 4a (y - k)`
And then we compare from the standard equation of parabola to find all its parameters.
(A) When the equation of parabola is : `(y -k)^2 = 4a(x - h)`
`(y -k)^2 = 4a(x - h)`................(i)
Equation (i) is of the form `Y^2 = 4aX`
where `Y = y - k` and `X = x - h`
(1) Axis of parabola is `Y = 0`, i.e., ` y - k = 0 => y = k`
(2) Coordinates of vertex of parabola are given by
`X=0` and `Y=0`
i.e, `x-h=0` and `y-k=0`
`:.` Vertex is `(h,k)`
(3) Tangent at the vertex to parabola (i) is given by
`X=0`, i. e. , `x - h = 0`
Therefore, tangent at the vertex is `x = h` .
(4) Coordinates of focus of parabola are given by
`X = a` and `Y = 0`
i.e. by `x - h = a` and `y - k = 0`
`:.` Focus of parabola is `(a + h, k)`.
(5) Equation of directrix of parabola is
`X =-a`
i.e., `x - h = -a`
Therefore, directrix of parabola is `x = h - a`
(6) Length of latus rectum of parabola is `|4a |`
(7) Coordinates of ends of latus rectum of parabola are given by
`X=a` & `Y=+-2a`
i.e., by `x-h=a` , `y-k=+-2a`
i.e., coordinate of latus rectum is `(a+h,k+-2a)`.
(8) Parametric equation is `x = h + at^2` and `y = k + 2at`.
(B) When the equation of parabola is :
`(x - h)^2 = 4a (y - k)` ........................(i)
Equation (i) is of the form `X^2 = 4aY`
where `X = x - h` and `Y = y - k`
(1) Axis of parabola is `X = 0`, i.e. , `x - h = 0`
(2) Coordinates of vertex of parabola is given by
`X = 0` and `Y = 0`
i.e. , by `x - h = 0` and `y - k = 0`
`:. x=h` and `y=k`
Hence vertex of parabola is `(h , k)`
(3) Equation of tangent at the vertex to parabola is
`Y = 0` i.e. , `y - k = 0`
or `y = k`
(4) Coordinates of focus of parabola are given by
`X=0` and `Y=a`
i.e., by `x-h=0` and `y-k=a`
`:.` Focus of Parabola is `(h,k+a)`.
(5) Equation of directrix of parabola (i) is given by
`Y =-a` or `y - k = - a` or `y = k - a`
(6) Length of latus rectum of parabola is `|4a |`.
(7) Coordinates of ends of latus rectum of parabola are given by
`Y=a` , `X=+-2a`
i.e., `y-k=a` , `X-h =+-2a`
`:.` Ends of latus ractum are `(h+-2a,k+a)`
(8) Parametric equation is `x=h+2at` and `y=k+at^2`