The force experienced by an object by physical contact is known as contact force.
e.g. Frictional force (which will be dealt in detail later), Normal force, tension.
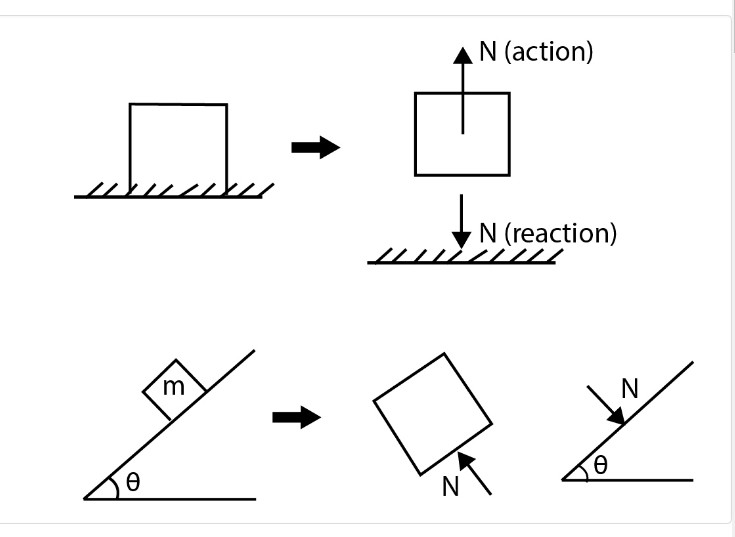
`(a)text(Normal force :)`
A contact force perpendicular (normal means perpendicular) to the contact surface that prevents two
objects from passing through one another is called the normal contact force.
`(b)text(Tension :)`
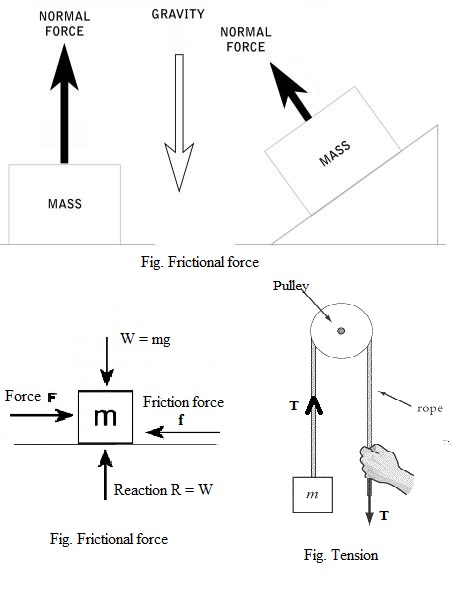
When a rope (string) is connected to a body and pulled taut, the rope is said to be under tension. It pulls the body with a force `T`, whose direction is away from the body and along the length of the rope. A rope is usually regarded to be massless and unstretchable. The rope exists only as a connections between two bodies. It pulls on the body at each end with the same magnitude of force `T`.
(i) If a string is massless, the tension in it is same everywhere. However, if a string has a mass, tension at different points may be different.
(ii) If there is friction between string and pulley, tension may be different on two sides of the pulley, but if there is no friction between pulley and string, tension will be same on both sides of the pulley.
(iii) If two persons are pulling a rope opposite to each other, each applying a force equal to `100 N`, then tension in the rope will be `100 N`.
`(c)text(Frictional force :)`
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other.
The frictional force acts along the contact surfaces.
The force experienced by an object by physical contact is known as contact force.
e.g. Frictional force (which will be dealt in detail later), Normal force, tension.
`(a)text(Normal force :)`
A contact force perpendicular (normal means perpendicular) to the contact surface that prevents two
objects from passing through one another is called the normal contact force.
`(b)text(Tension :)`
When a rope (string) is connected to a body and pulled taut, the rope is said to be under tension. It pulls the body with a force `T`, whose direction is away from the body and along the length of the rope. A rope is usually regarded to be massless and unstretchable. The rope exists only as a connections between two bodies. It pulls on the body at each end with the same magnitude of force `T`.
(i) If a string is massless, the tension in it is same everywhere. However, if a string has a mass, tension at different points may be different.
(ii) If there is friction between string and pulley, tension may be different on two sides of the pulley, but if there is no friction between pulley and string, tension will be same on both sides of the pulley.
(iii) If two persons are pulling a rope opposite to each other, each applying a force equal to `100 N`, then tension in the rope will be `100 N`.
`(c)text(Frictional force :)`
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other.
The frictional force acts along the contact surfaces.