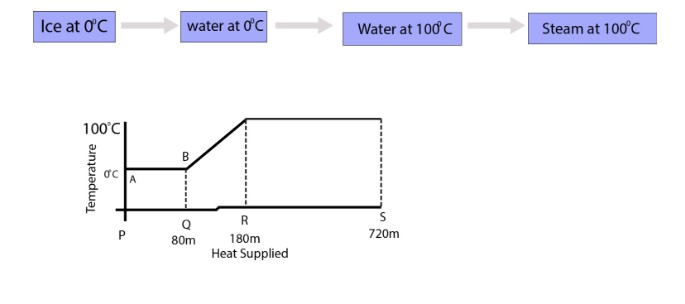
Journey from ice at `0^0C` to steam at `100^0C`
`Q=mL_V`
`Q=ms Delta T`
`Q=mL_F`
Suppose mass of ice is `m` gram. During state change from ice to water at `0^0C`, ice absorbed heat `(Q) = mL_F`. After that temperature of water increases and water consumes heat `(Q) = ms Delta T` (where `Delta T = 100^0C`). Now water at `100^0 C` converts
into steam at `100^0C` and absorbed heat `(Q) = mL_V`.
`Q=ms Delta T`
`Q=mL_F`
Suppose mass of ice is `m` gram. During state change from ice to water at `0^0C`, ice absorbed heat `(Q) = mL_F`. After that temperature of water increases and water consumes heat `(Q) = ms Delta T` (where `Delta T = 100^0C`). Now water at `100^0 C` converts
into steam at `100^0C` and absorbed heat `(Q) = mL_V`.