Physical Properties :
1. Physical state, colour and odour: Dimethyl and ethyl methyl ethers are gases at ordinary temperature while the other lower homologues of ethers are colourless liquid with characteristic 'ether smell'.
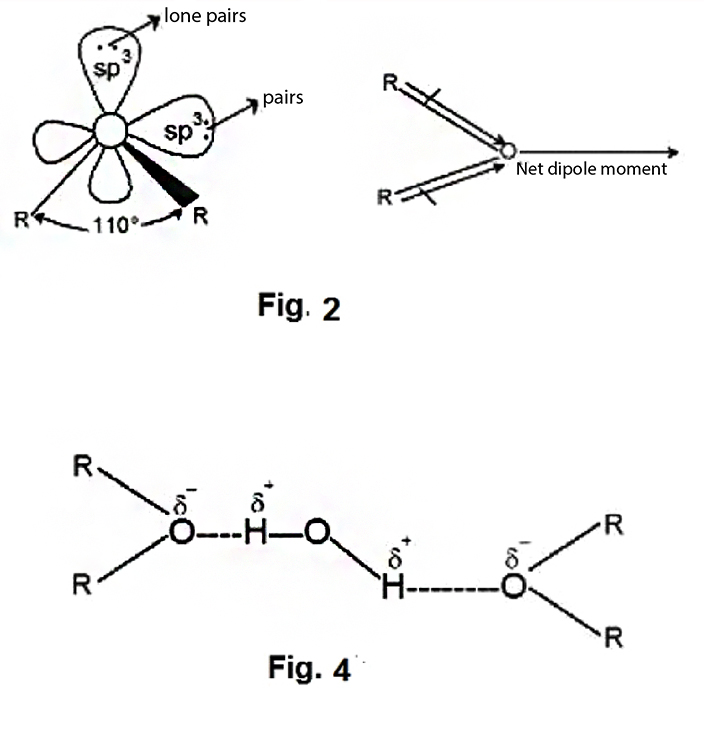
2. Dipole nature: Ethers have a tetrahedral geometry i.e., oxygen is `sp^3` hybridized. The `C- O - C` angle in ethers is `110^o`. Because of the greater electronegativity of oxygen than carbon, the `C-O` bonds are slightly polar and are inclined to each other at an angle of `110^o`, resulting in a net dipole moment the Fig 2 showing Diople moment.
3. Bond angle of ether is greater than that of tetrahedral bond angle of `109^o28` . This is due to the fact that internal repulsion by the hydrocarbon part is greater than the external repulsion of the lone pair on oxygen. If the size of the hydrocarbon part increases, then the bond angle also increases slightly and vice - versa.
4. Solubility and boiling point: Due to the formation of less degree of hydrogen bonding, ethers have lower boiling point than their corresponding isomeric alcohols and are slightly soluble in water. Upto `C_4` (on both side of `- O -` ) ether is soluble in water being polar, Shown in Fig. 4.
Moreover, others are fairly soluble in common organic solvents like alcohols, benzene chloroform, acetone etc.
5. Ethers are polar as well as non polar. Alkyl groups in an ether act as a hydrophobic part whereas oxygen acts as a hydrophilic part. If the hydrophilic part is dominant over the hydrophobic part, then ether will be polar. As the size of the hydrophobic part increases, the ether becomes non polar .
2. Dipole nature: Ethers have a tetrahedral geometry i.e., oxygen is `sp^3` hybridized. The `C- O - C` angle in ethers is `110^o`. Because of the greater electronegativity of oxygen than carbon, the `C-O` bonds are slightly polar and are inclined to each other at an angle of `110^o`, resulting in a net dipole moment the Fig 2 showing Diople moment.
3. Bond angle of ether is greater than that of tetrahedral bond angle of `109^o28` . This is due to the fact that internal repulsion by the hydrocarbon part is greater than the external repulsion of the lone pair on oxygen. If the size of the hydrocarbon part increases, then the bond angle also increases slightly and vice - versa.
4. Solubility and boiling point: Due to the formation of less degree of hydrogen bonding, ethers have lower boiling point than their corresponding isomeric alcohols and are slightly soluble in water. Upto `C_4` (on both side of `- O -` ) ether is soluble in water being polar, Shown in Fig. 4.
Moreover, others are fairly soluble in common organic solvents like alcohols, benzene chloroform, acetone etc.
5. Ethers are polar as well as non polar. Alkyl groups in an ether act as a hydrophobic part whereas oxygen acts as a hydrophilic part. If the hydrophilic part is dominant over the hydrophobic part, then ether will be polar. As the size of the hydrophobic part increases, the ether becomes non polar .