Alkyl Halides :
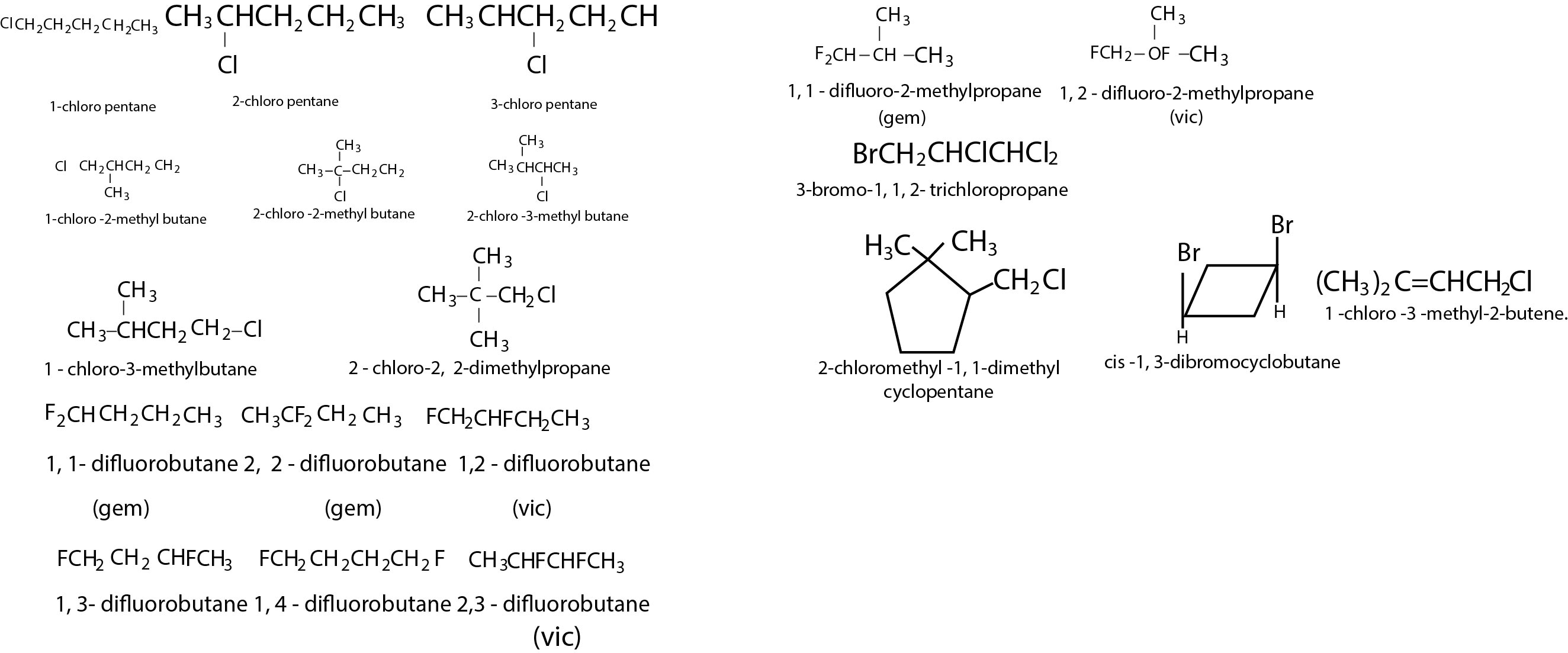
Alkyl halides are halogen substituted alkanes. A monohaloalkane is written as `R - X`, where `X` is any halogen atom (`F, Cl, Br` and `I` ). The general formula of monohaloalkanes is `C_nH_(2n + 1)X` while that of a dihaloalkane is `C_nH_(2n)X_2` .
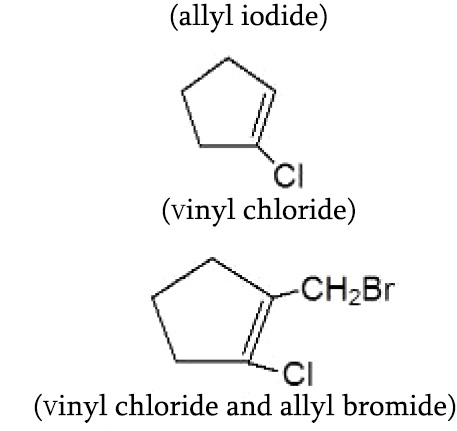
Alkyl halides of a particular kind, in which halogen atom is attached to a saturated carbon, which in turn is linked to unsaturated carbon, are called allyl halides. And when halogen atom is attached to an unsaturated `(sp^2)` carbon, they are called vinyl halides. For example,
`H_2C=CHCH_(2) - I `
Alkyl halides are classified as primary `(1^(circ))`, secondary `(2^(circ) )` or tertiary `(3^(circ) )`, depending upon the type of carbon to which `X` is bonded. When `X` is bonded to a carbon, which is bonded to one more carbon is called `1^(circ)` halide and their general representation is `RCH_2X`. When `X` is linked to a carbon, which is bonded to two carbons is called `2^(circ)` halides and is denoted by `R_2CHX`. When `X` is bonded to a carbon, which is attached to `3` carbons is called `3^(circ)` halides and is designated as `R_3CX`. `CH_3X` is unique (not classified as `1^(circ), 2^(circ)` or `3^(circ)`) as carbon is bonded to only hydrogens and is simply called methyl halide. Dihaloalkanes with both halogens on same carbon are called gemdihalides and with halogen on adjacent carbons are called vicinal dihalides.
Alkyl halides of a particular kind, in which halogen atom is attached to a saturated carbon, which in turn is linked to unsaturated carbon, are called allyl halides. And when halogen atom is attached to an unsaturated `(sp^2)` carbon, they are called vinyl halides. For example,
`H_2C=CHCH_(2) - I `
Alkyl halides are classified as primary `(1^(circ))`, secondary `(2^(circ) )` or tertiary `(3^(circ) )`, depending upon the type of carbon to which `X` is bonded. When `X` is bonded to a carbon, which is bonded to one more carbon is called `1^(circ)` halide and their general representation is `RCH_2X`. When `X` is linked to a carbon, which is bonded to two carbons is called `2^(circ)` halides and is denoted by `R_2CHX`. When `X` is bonded to a carbon, which is attached to `3` carbons is called `3^(circ)` halides and is designated as `R_3CX`. `CH_3X` is unique (not classified as `1^(circ), 2^(circ)` or `3^(circ)`) as carbon is bonded to only hydrogens and is simply called methyl halide. Dihaloalkanes with both halogens on same carbon are called gemdihalides and with halogen on adjacent carbons are called vicinal dihalides.