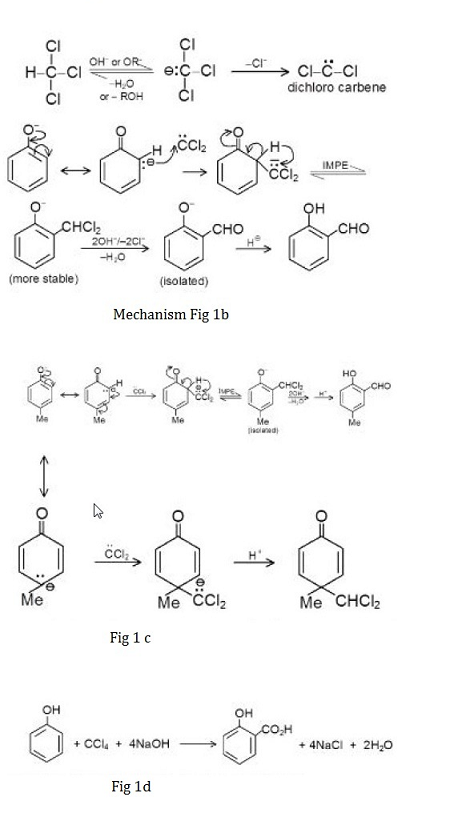
Reimer -Tiemann Reaction :
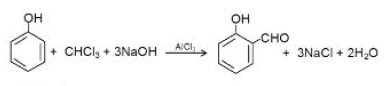
An alkaline solution of phenol is refluxed with chloroform at `60^oC`, distilling off the excess of chloroform and acidifying the residual liquid with sulphuric acid. As a result, `o` - hydroxy and `p`- hydroxy benzaldehyde are formed, which are separated by steam- distillation.