Types of Flow
`text(Steady Flow :)`
A flow in which velocity, pressure and density at a given point do not change with time.
`(dv)/(dt) =0 , (dp)/(dt) = 0`
`text(Unsteady Flow :)`
A flow in which velocity at a point varies with time.
`(dv)/(dt) ne 0`
`text(Streamline Flow :)`
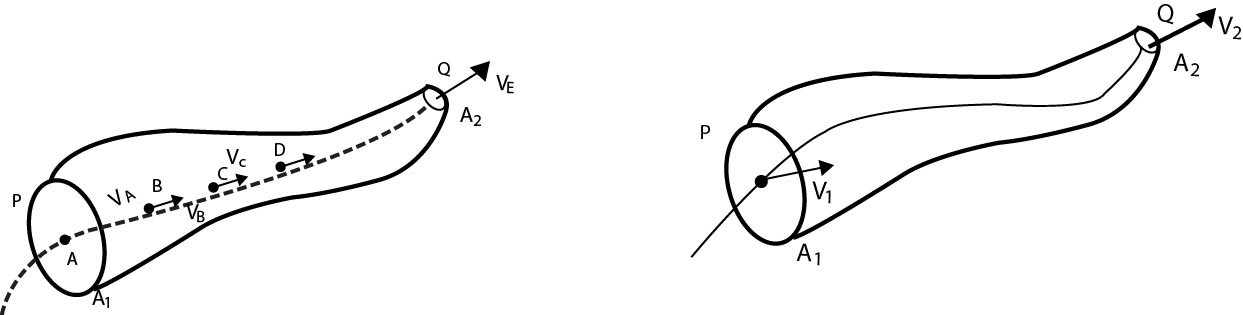
Consider an incompressible, non-viscous fluid flowing through a rube. Take a line `A - B - C - D - E` through which fluid particles are successively following each other move from `A` to E.
Let the velocities of fluid particles of `A, B , C , D , E` are respectively `vecv_A,vecv_B,vecv_C,vecv_D,vecv_E`
In a steady flow, `vecv_A,vecv_B,vecv_C,vecv_D` and `vecv_E` are constant with time.
When a fluid particle is coming towards `A`, just reaches `A` and then acquires the velocity `vecv_A`, .
In this way successively the fluid particle while reaching `B, C, D` and `E` acquires the velocities `vecv_B,vecv_C,vecv_D` and `vecv_E` respectively.
This reveals that line of motion of a stream of fluid particles is a fixed and the velocities at different points are fixed with respect to time.
This path of motion of fluid particles is called a streamline and the motion is called Streamline flow.
`text(Turbulent Flow :)`
Turbulent flow is a type of fluid (gas or liquid) flow in which the fluid undergoes irregular fluctuations, or mixing, in contrast to laminar flow, in which the fluid moves in smooth paths or layers. In turbulent flow the speed of the fluid at a point is continuously undergoing changes in both magnitude and direction.
The flow of wind and rivers is generally turbulent in this sense, even if the currents are gentle. The air or water swirls and eddies while its overall bulk moves along a specific direction.
Most kinds of fluid flow are turbulent, except for laminar flow at the leading edge of solids moving relative to fluids or extremely close to solid surfaces, such as the inside wall of a pipe, or in cases of fluids of high viscosity (relatively great sluggishness) flowing slowly through small channels. Common examples of turbulent flow are blood flow in arteries, oil transport in pipelines, lava flow, atmosphere and ocean currents, the flow through pumps and turbines, and the flow in boat wakes and around aircraft-wing tips.
`=>` Re > 4000
`=>` 'high' velocity
`=>` Dye mixes rapidly and completely
`=>` Particle paths completely irregular
`=>` Average motion is in the direction of the flow
`=>` Cannot be seen by the naked eye
`=>` Changes/fluctuations are very difficult to detect. Must use laser.
`=>` Mathematical analysis very difficult - so experimental measures are used
`=>` Most common type of flow.
A flow in which velocity, pressure and density at a given point do not change with time.
`(dv)/(dt) =0 , (dp)/(dt) = 0`
`text(Unsteady Flow :)`
A flow in which velocity at a point varies with time.
`(dv)/(dt) ne 0`
`text(Streamline Flow :)`
Consider an incompressible, non-viscous fluid flowing through a rube. Take a line `A - B - C - D - E` through which fluid particles are successively following each other move from `A` to E.
Let the velocities of fluid particles of `A, B , C , D , E` are respectively `vecv_A,vecv_B,vecv_C,vecv_D,vecv_E`
In a steady flow, `vecv_A,vecv_B,vecv_C,vecv_D` and `vecv_E` are constant with time.
When a fluid particle is coming towards `A`, just reaches `A` and then acquires the velocity `vecv_A`, .
In this way successively the fluid particle while reaching `B, C, D` and `E` acquires the velocities `vecv_B,vecv_C,vecv_D` and `vecv_E` respectively.
This reveals that line of motion of a stream of fluid particles is a fixed and the velocities at different points are fixed with respect to time.
This path of motion of fluid particles is called a streamline and the motion is called Streamline flow.
`text(Turbulent Flow :)`
Turbulent flow is a type of fluid (gas or liquid) flow in which the fluid undergoes irregular fluctuations, or mixing, in contrast to laminar flow, in which the fluid moves in smooth paths or layers. In turbulent flow the speed of the fluid at a point is continuously undergoing changes in both magnitude and direction.
The flow of wind and rivers is generally turbulent in this sense, even if the currents are gentle. The air or water swirls and eddies while its overall bulk moves along a specific direction.
Most kinds of fluid flow are turbulent, except for laminar flow at the leading edge of solids moving relative to fluids or extremely close to solid surfaces, such as the inside wall of a pipe, or in cases of fluids of high viscosity (relatively great sluggishness) flowing slowly through small channels. Common examples of turbulent flow are blood flow in arteries, oil transport in pipelines, lava flow, atmosphere and ocean currents, the flow through pumps and turbines, and the flow in boat wakes and around aircraft-wing tips.
`=>` Re > 4000
`=>` 'high' velocity
`=>` Dye mixes rapidly and completely
`=>` Particle paths completely irregular
`=>` Average motion is in the direction of the flow
`=>` Cannot be seen by the naked eye
`=>` Changes/fluctuations are very difficult to detect. Must use laser.
`=>` Mathematical analysis very difficult - so experimental measures are used
`=>` Most common type of flow.