Interatomic and Intermolecular forces :
Atoms and molecules of matter are held together by
interatomic or intermolecular forces.
They are electrical in nature and hence can be
attractive or repulsive.
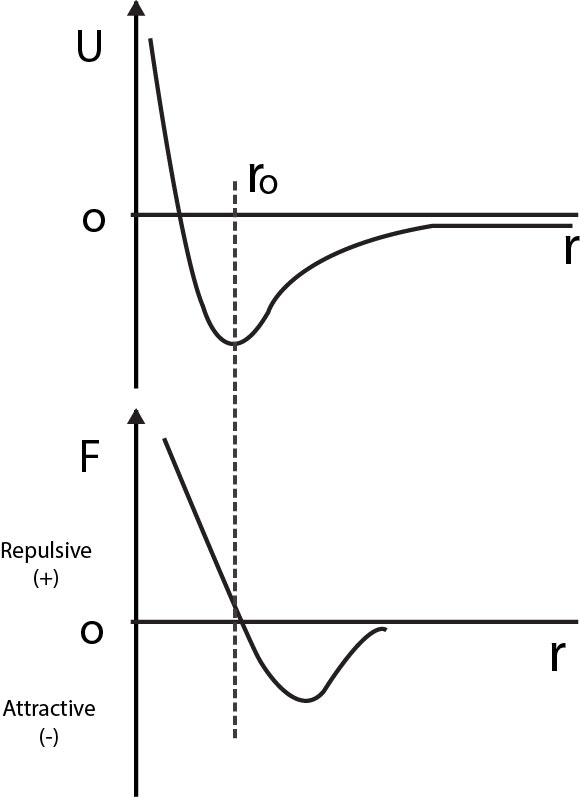
The mutual potential energy (U) corresponding to this
force between two molecules or atoms as a function of
their separation(r) is shown.
The corresponding force between two molecules
` F = - (dU)/(dr)`
The potential energy is a minimum at the equilibrium
separation `r_0` , at which point the force is zero.
As the separation `(r)` decreases, the attractive force
first increases and then decreases to zero at `r = r_0` .
For smaller distances force is repulsive.
interatomic or intermolecular forces.
They are electrical in nature and hence can be
attractive or repulsive.
The mutual potential energy (U) corresponding to this
force between two molecules or atoms as a function of
their separation(r) is shown.
The corresponding force between two molecules
` F = - (dU)/(dr)`
The potential energy is a minimum at the equilibrium
separation `r_0` , at which point the force is zero.
As the separation `(r)` decreases, the attractive force
first increases and then decreases to zero at `r = r_0` .
For smaller distances force is repulsive.