Introduction and Nomenclature :
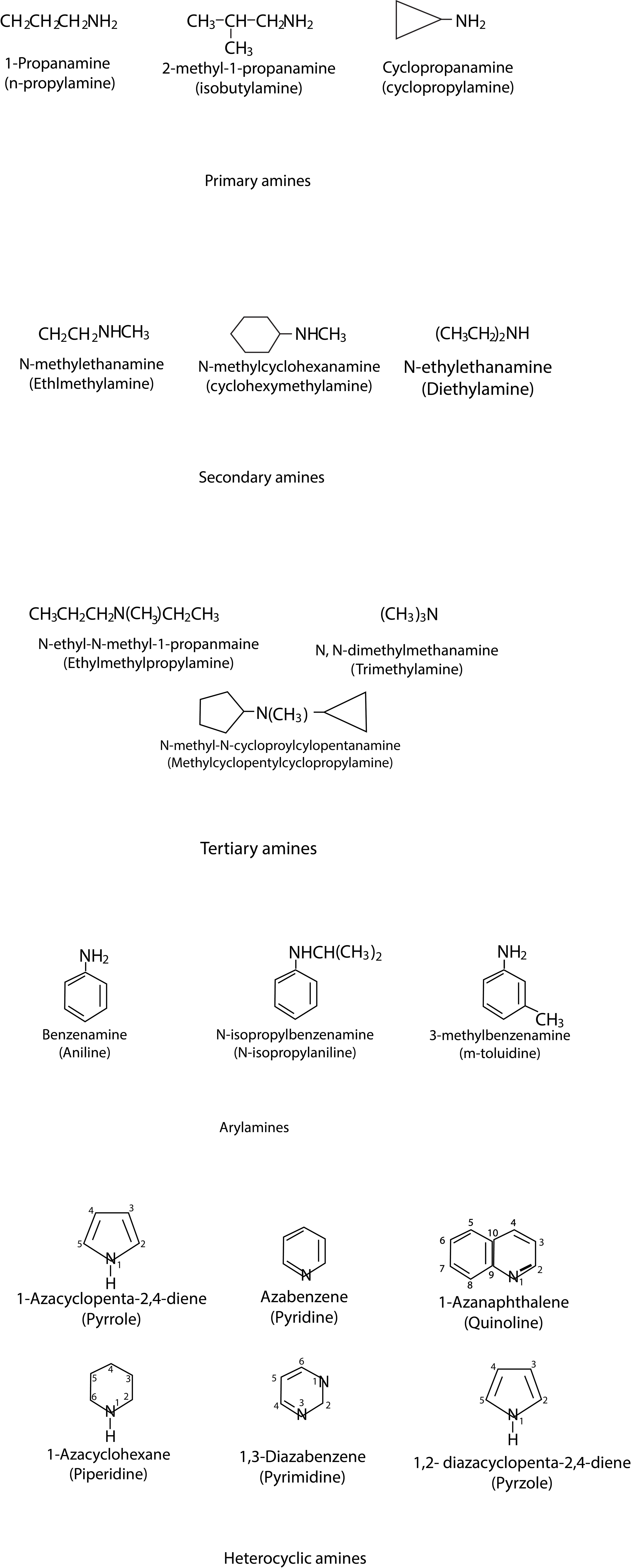
Amines are organic compounds of ammonia in which one or more than one hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms or group of atoms. They are classified as primary (`RNH_2` or `1^(o)`), secondary (`R_2NH` or `2^(o)`) or tertiary (`R_3N` or `3^(o)`) depending upon one, two or all the three hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl groups (`R`).
Amines are commonly named as alkyl amines. The alkyl groups attached to `N`-atom are named in the alphabetical order followed by amine. According to IUPAC system of nomenclature they are named as Alkanamine . The longest carbon atom chain attached to `N`-atom is chosen as the parent compound and in the name of parent hydrocarbon, the last letter 'e' is replaced by the suffix amine. The substituents are named as prefixes in the alphabetical order. The IUPAC names (in bold letters) and common names (in parenthesis) of some of the well known amines are given below.
(A) Primary amines :
(B) Secondary amines:
(C) Tertiary amines:
(D) Arylamines: Arylamines have `-NH_2` group directly attached to the benzene ring. They are named as derivatives of aniline (common name) or benzenamine (IUPAC name).
(E) Heterocyclic amines: IUPAC names of heterocyclic amines have prefixes aza, diaza or triaza to indicate one, two or three nitrogen atoms have replaced carbon atoms in the corresponding hydrocarbons. Numbering of the ring starts from the hetero atom. The names of some of the well known heterocyclic amines are as follows:
Amines are commonly named as alkyl amines. The alkyl groups attached to `N`-atom are named in the alphabetical order followed by amine. According to IUPAC system of nomenclature they are named as Alkanamine . The longest carbon atom chain attached to `N`-atom is chosen as the parent compound and in the name of parent hydrocarbon, the last letter 'e' is replaced by the suffix amine. The substituents are named as prefixes in the alphabetical order. The IUPAC names (in bold letters) and common names (in parenthesis) of some of the well known amines are given below.
(A) Primary amines :
(B) Secondary amines:
(C) Tertiary amines:
(D) Arylamines: Arylamines have `-NH_2` group directly attached to the benzene ring. They are named as derivatives of aniline (common name) or benzenamine (IUPAC name).
(E) Heterocyclic amines: IUPAC names of heterocyclic amines have prefixes aza, diaza or triaza to indicate one, two or three nitrogen atoms have replaced carbon atoms in the corresponding hydrocarbons. Numbering of the ring starts from the hetero atom. The names of some of the well known heterocyclic amines are as follows: