Bulk Modulus of Elasticity (B or K)
It is the ratio of normal stress to volumetric strain, within proportional limit.
`B` or `K = ` `text(Normal stress)/text(Volumetrics strain)`
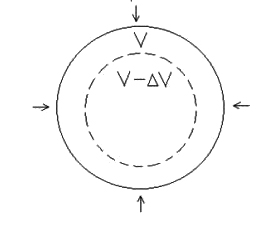
Consider a spherical solid body of volume (V) and surface area (A). In order to compress the body, suppose a pressure (P) is applied on the body which decreases its volume by Delta `(Delta V)` as shown. The volumetric strain is given by
`in_V = (Delta V)/V`
Negative sign shows that volume is decreasing when pressure is applied.
Normal stress `= P =` Pressure applied
`B = P/(_(DeltaV)//V) = -(PV)/(DeltaV)`
`B` is a constant and is known as the Bulk modulus of elasticity.
`S.l.` unit of `B` is `N//m^2` or `Pa` .
The object is said to be under hydraulic compression and the pressure can be called the hydraulic stress.
Bulk modulus of solids is about 50 times to that of liquids and for gases it is `10^(-8)` times to that of solids.
`B_(solids) > B_(Liquids) > B_(gases)`
For gases, there are two types of Bulk modulii
`text(Isothermal Bulk modulus of elasticity of gas :)`
`B_(iso) = P` (Pressure of gas)
`text(Adiabatic Bulk modulus of elasticity of gas :)`
`B_(adi) = gamma P`
`P=` Pressure of gas `gamma = (C_p)/(C_v)`
`B` or `K = ` `text(Normal stress)/text(Volumetrics strain)`
Consider a spherical solid body of volume (V) and surface area (A). In order to compress the body, suppose a pressure (P) is applied on the body which decreases its volume by Delta `(Delta V)` as shown. The volumetric strain is given by
`in_V = (Delta V)/V`
Negative sign shows that volume is decreasing when pressure is applied.
Normal stress `= P =` Pressure applied
`B = P/(_(DeltaV)//V) = -(PV)/(DeltaV)`
`B` is a constant and is known as the Bulk modulus of elasticity.
`S.l.` unit of `B` is `N//m^2` or `Pa` .
The object is said to be under hydraulic compression and the pressure can be called the hydraulic stress.
Bulk modulus of solids is about 50 times to that of liquids and for gases it is `10^(-8)` times to that of solids.
`B_(solids) > B_(Liquids) > B_(gases)`
For gases, there are two types of Bulk modulii
`text(Isothermal Bulk modulus of elasticity of gas :)`
`B_(iso) = P` (Pressure of gas)
`text(Adiabatic Bulk modulus of elasticity of gas :)`
`B_(adi) = gamma P`
`P=` Pressure of gas `gamma = (C_p)/(C_v)`