1. Trioses : Number of carbons = 3 (Simplest monosaccharide)
# common formulae `= C_(3) H_(6)O_(3)`
e.g. DHAP , PGAL
2. Tetroses: Number of carbons= 4
# Common Formulae `=C_(4)H_(8)O_(4)`
e.g. Erythrose, Erythrulose
3 . Pentose : Number of carbons = 5
# Common Formulae `= C_(5)H_(10)O_(5)`
e.g. Xylose
Xylulose
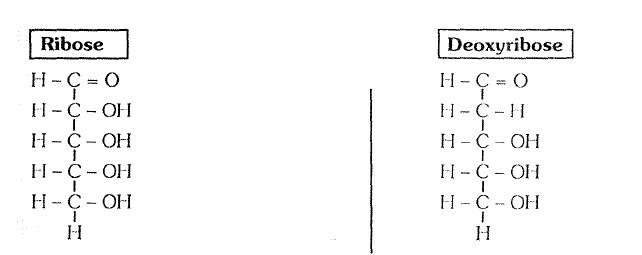
Deoxyribose
Arabinose
Ribose
Ribulose
# Present in RNA, ATP, FAD, FMN, NAD # Present in DNA
# Molecular Formulae `= C_(5)H_(10)O_(5)` #Molecular formulae `= C_(5)H_(10)o_( 4)` (Exception)
4. Hexoses : Number of carbons `= 6`
Common Formulae `= C_(6)H(12)O_(6)`
e.g. Rhamnose
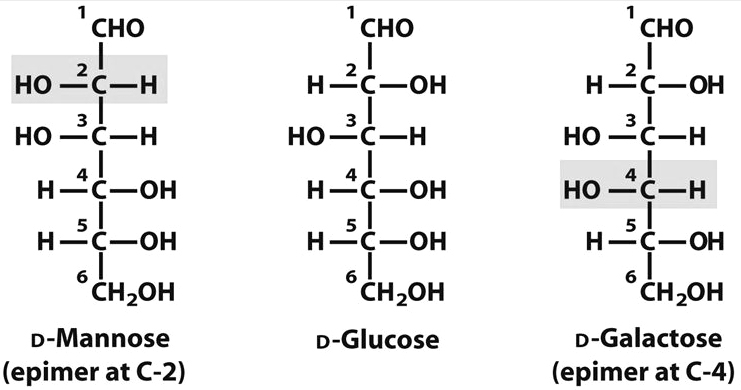
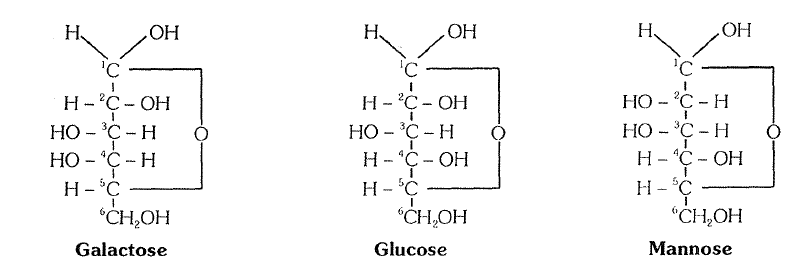
Mannose
Galactose
Glucose
Fructose
Glucose : More abundant in grapes so also known as grape sugar.
# More abundant in blood so known as blood sugar.
# Main respiratory substance.
# It rotates PPL in right direction so it is dextrorotatory and also known as dextrose.
Fructose:
# Sweetest carbohydrate
# More abundant in honey and sweet fruits so also known as fruit sugar.
# Rotates PPL in left direction so it is laevorotatory and also known as 'Laevulose'.
# Thaumatine is sweetest chemical substance which is obtained from Thaumatococcus danielli bacteria.
# Aspartame/Aspartin is most commonly used artificial sweetener. It is non carcinogenic.
Galactose:
# Most abundant in brain and nervous tissue so called as 'brain sugar'.
# It never occurs in free form. 11 always occurs as a component of some compounds.
e.g. Hemicellulose, Lactose, Pectin, Clycolipid
Mannose:
# It also never occurs in free form.
# It is present as a component of some compounds.
e.g. Albumen- Egg
Hemicellulose - Wood
Rhamnose:
# One oxygen atom is deficient in it's structure so molecular formulae is `C_(6)H_(12)O_( 5)` (Exception)
# Present in phloem.
5. Heptoses : Number of carbons `= 7` (Largest monosaccharide)
Common formulae `= C_(7)H_(14)O_(7)`
e.g. Sedoheptulose
# Monosaccharides with free aldehyde group are termed as Aldoses (PGAL, Erythrose, H.ibose, Arabinose, Deoxyribose, Clucose, Galactose, Mannose).
# While monosaccharides with free ketone group are called ketoses (DHAP, Erythrulose, Ribulose, xylulose, Fructose, Sedoheptulose).
All monosaccharides are "reducing sugars" as their free aldehyde or ketone groups are capable of reducing `Cu^(++)` to `Cu^(+)`.
This property is the basis of Benedict's test or fehling's test used to detect the presence of glucose in urine.
1. Trioses : Number of carbons = 3 (Simplest monosaccharide)
# common formulae `= C_(3) H_(6)O_(3)`
e.g. DHAP , PGAL
2. Tetroses: Number of carbons= 4
# Common Formulae `=C_(4)H_(8)O_(4)`
e.g. Erythrose, Erythrulose
3 . Pentose : Number of carbons = 5
# Common Formulae `= C_(5)H_(10)O_(5)`
e.g. Xylose
Xylulose
Deoxyribose
Arabinose
Ribose
Ribulose
# Present in RNA, ATP, FAD, FMN, NAD # Present in DNA
# Molecular Formulae `= C_(5)H_(10)O_(5)` #Molecular formulae `= C_(5)H_(10)o_( 4)` (Exception)
4. Hexoses : Number of carbons `= 6`
Common Formulae `= C_(6)H(12)O_(6)`
e.g. Rhamnose
Mannose
Galactose
Glucose
Fructose
Glucose : More abundant in grapes so also known as grape sugar.
# More abundant in blood so known as blood sugar.
# Main respiratory substance.
# It rotates PPL in right direction so it is dextrorotatory and also known as dextrose.
Fructose:
# Sweetest carbohydrate
# More abundant in honey and sweet fruits so also known as fruit sugar.
# Rotates PPL in left direction so it is laevorotatory and also known as 'Laevulose'.
# Thaumatine is sweetest chemical substance which is obtained from Thaumatococcus danielli bacteria.
# Aspartame/Aspartin is most commonly used artificial sweetener. It is non carcinogenic.
Galactose:
# Most abundant in brain and nervous tissue so called as 'brain sugar'.
# It never occurs in free form. 11 always occurs as a component of some compounds.
e.g. Hemicellulose, Lactose, Pectin, Clycolipid
Mannose:
# It also never occurs in free form.
# It is present as a component of some compounds.
e.g. Albumen- Egg
Hemicellulose - Wood
Rhamnose:
# One oxygen atom is deficient in it's structure so molecular formulae is `C_(6)H_(12)O_( 5)` (Exception)
# Present in phloem.
5. Heptoses : Number of carbons `= 7` (Largest monosaccharide)
Common formulae `= C_(7)H_(14)O_(7)`
e.g. Sedoheptulose
# Monosaccharides with free aldehyde group are termed as Aldoses (PGAL, Erythrose, H.ibose, Arabinose, Deoxyribose, Clucose, Galactose, Mannose).
# While monosaccharides with free ketone group are called ketoses (DHAP, Erythrulose, Ribulose, xylulose, Fructose, Sedoheptulose).
All monosaccharides are "reducing sugars" as their free aldehyde or ketone groups are capable of reducing `Cu^(++)` to `Cu^(+)`.
This property is the basis of Benedict's test or fehling's test used to detect the presence of glucose in urine.