Types of Oligosaccharides :-
(i) Disaccharides- composed of two monosaccharide units. e.g. Maltose, Sucrose, Lactose, Trehalose.
# All disaccharides are water soluble and sweet in taste, so they are known as sugar.
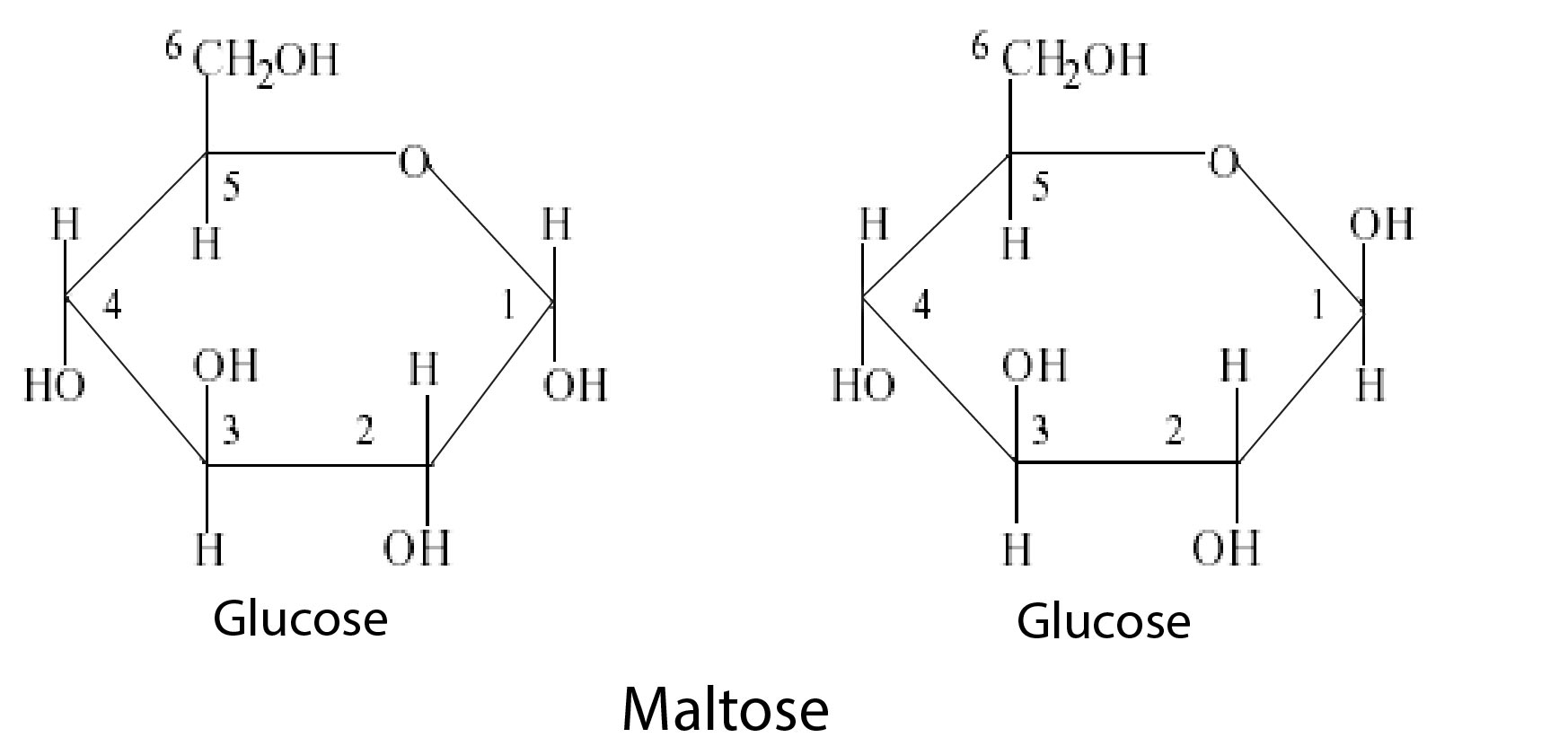
# Maltose is commonly called malt sugar. It is intermediate compound in starch digestion. Maltose has 1'
glycosidic linkage between `alpha-D` glucose and `alpha-D` glucose
# Lactose is milk sugar with `beta -1'-4" `glycosidic linkage between glucose and galactose
# Lactose is least sweetest sugar.
# Maximum % of lactose = Human milk ` approx 7%`
# In plants transport of sugar is present in form of sucrose.
# Sucrose is also known as invert sugar.
# Sucrose is called Cane Sugar or Table Sugar or Commercial Sugar. Sucrose composed of `alpha-D` Glucose and
fructose.
# Trehalose is present in haemolymph of insects. It has glycosidic linkage between two anomeric carbon (`alpha-` glucose and `beta-` gluocse).
(ii) Trisaccharides - e.g. Raffi nose ( Calacfose -t-Clucose +Fructose)
(iii) Tetrasaccharides - e.g Stachyose (Gal. + Gal. + Glu. + Fructose)
(iv) Pentasaccharides - e.g Verbascose (Gal. + Gal. + Gal. Gu + Fructose)
Raffinose and stachyose occur in phloem and may be enwloyed for lrcmslocation of carbohydrates.
# All disaccharides are water soluble and sweet in taste, so they are known as sugar.
# Maltose is commonly called malt sugar. It is intermediate compound in starch digestion. Maltose has 1'
glycosidic linkage between `alpha-D` glucose and `alpha-D` glucose
# Lactose is milk sugar with `beta -1'-4" `glycosidic linkage between glucose and galactose
# Lactose is least sweetest sugar.
# Maximum % of lactose = Human milk ` approx 7%`
# In plants transport of sugar is present in form of sucrose.
# Sucrose is also known as invert sugar.
# Sucrose is called Cane Sugar or Table Sugar or Commercial Sugar. Sucrose composed of `alpha-D` Glucose and
fructose.
# Trehalose is present in haemolymph of insects. It has glycosidic linkage between two anomeric carbon (`alpha-` glucose and `beta-` gluocse).
(ii) Trisaccharides - e.g. Raffi nose ( Calacfose -t-Clucose +Fructose)
(iii) Tetrasaccharides - e.g Stachyose (Gal. + Gal. + Glu. + Fructose)
(iv) Pentasaccharides - e.g Verbascose (Gal. + Gal. + Gal. Gu + Fructose)
Raffinose and stachyose occur in phloem and may be enwloyed for lrcmslocation of carbohydrates.