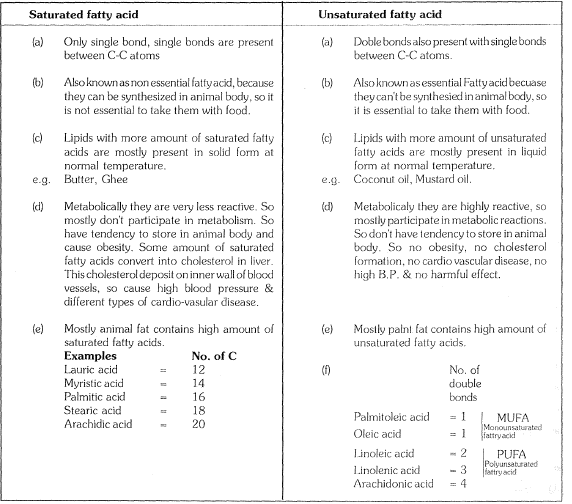
(1) Phospholipids or phosphatide or phospholipins :-
2 Molecules of fatty acid + c;Jycerol + `H_(3)PO_(4)` + Nitrogenous compound. Phospholipids are most abun·
dant type of lipids in protoplasm.
Phospholipids have both hydrophilic polar end (`H_(3)PO_( 4)` and nitrogenous compound) and hydrophobic non
polar end (fatty acids). Such molecules are called amphipathic. Due to this property, phospholipids form
bimolecular layer in cell membrane.
Some biologically important phospholipids are as following :
(a) Lecithin or Phosphatidyl choline
`->` Nitrogenous compound in lecithin is choline
`->` Lecithin occurs in egg yolk, oil seeds and blood.
`->` In blood lecithin functions as carrier molecule. It helps in transportation of other lipid.
(b) Cephalin-Similar to lecithin but the nitrogenous compound is ethanolamine, cephalin occurs in nervous tissue, egg yolk and blood platelets.
(c) Sphingolipid.s or sphingomyelins similar to lecithin but in place of Blycerol it contains an amino alcohol sphingosine.
Sphingolipids occur in myelin- sheath of nerves, other examples of phospholipid are phosphatidyl
serine, phosphatidyl inositol, plasmologens.
(2) Glycolipid :- 2 fatty acid + sphingosine + galactose
eg. Cerebroiside which occurs in white matter of brain
Gangliosides -These occur in nerve ganglia and spleen. These also contain N-acetyl neuromink
acid and glucose beside other compounds.
(3) Derived Lipids ~- Lipid derived from simple or conjugated lipid .Derived lipids are complex in struc
ture. They are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents
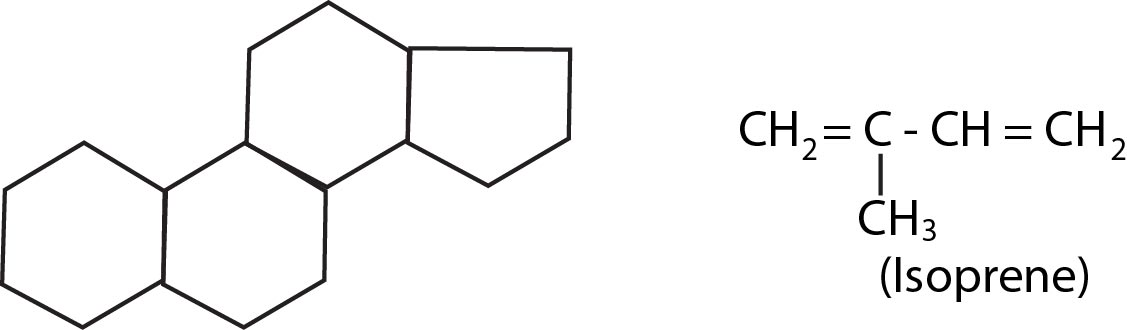
(1) Steroids :- Steroids exhibit tetracyclic structure called "Cydo pentano perhydrophenanthrene nucleus" On the basis of functional group, steroids are of two types-
(a) Sterols:- Alcoholic steroids e.g. cholesterol- Cholesterol abundantly occurs in brain, nervous tissue , Adrenal gland and skin. Cholesterol is a parent steroid. Several other biologically important steroids are derived from cholesterol 7 dehydrocholesterol which occurs in skin is a provitamin. On exposure to ultraviolet radiation, it transforms in cholecalciferol i. e vitamin D
`->` Cholesterol is also called "most decorated micromolecule in biology".
Ergosterol :-It occurs in oil seed , fungi like ergot and yeast . Ergosterol is precursor of another form of Vitamin D-Ergocalciferol.
Coprosterol :-Occurs in faecal matter. It forms by decomposition of cholesterol by colon bacteria
Bile acid:- Bile Juice contains different types of steroid acids. e. g. cholic acid. Lithocholic acid etc.
They help in emulsification of fats.
(b) Sterones :- Ketonic steroids, for e. g. sex hormones, Adreno corticoids , ecdyson hormone of insects,Diosgenin obtained from yam plant (Dioscorea), is used in manufacture of antifertility pills.
(2) Chromolipid = It is also called terpene.
`->` Most complex lipid in protoplasm.
`->` Chromolipids composed of repeated isoprene units
Example : Carotenoids, vitamin `A, E, K`, Natural Hubber (Polyterpene)
(1) Phospholipids or phosphatide or phospholipins :-
2 Molecules of fatty acid + c;Jycerol + `H_(3)PO_(4)` + Nitrogenous compound. Phospholipids are most abun·
dant type of lipids in protoplasm.
Phospholipids have both hydrophilic polar end (`H_(3)PO_( 4)` and nitrogenous compound) and hydrophobic non
polar end (fatty acids). Such molecules are called amphipathic. Due to this property, phospholipids form
bimolecular layer in cell membrane.
Some biologically important phospholipids are as following :
(a) Lecithin or Phosphatidyl choline
`->` Nitrogenous compound in lecithin is choline
`->` Lecithin occurs in egg yolk, oil seeds and blood.
`->` In blood lecithin functions as carrier molecule. It helps in transportation of other lipid.
(b) Cephalin-Similar to lecithin but the nitrogenous compound is ethanolamine, cephalin occurs in nervous tissue, egg yolk and blood platelets.
(c) Sphingolipid.s or sphingomyelins similar to lecithin but in place of Blycerol it contains an amino alcohol sphingosine.
Sphingolipids occur in myelin- sheath of nerves, other examples of phospholipid are phosphatidyl
serine, phosphatidyl inositol, plasmologens.
(2) Glycolipid :- 2 fatty acid + sphingosine + galactose
eg. Cerebroiside which occurs in white matter of brain
Gangliosides -These occur in nerve ganglia and spleen. These also contain N-acetyl neuromink
acid and glucose beside other compounds.
(3) Derived Lipids ~- Lipid derived from simple or conjugated lipid .Derived lipids are complex in struc
ture. They are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents
(1) Steroids :- Steroids exhibit tetracyclic structure called "Cydo pentano perhydrophenanthrene nucleus" On the basis of functional group, steroids are of two types-
(a) Sterols:- Alcoholic steroids e.g. cholesterol- Cholesterol abundantly occurs in brain, nervous tissue , Adrenal gland and skin. Cholesterol is a parent steroid. Several other biologically important steroids are derived from cholesterol 7 dehydrocholesterol which occurs in skin is a provitamin. On exposure to ultraviolet radiation, it transforms in cholecalciferol i. e vitamin D
`->` Cholesterol is also called "most decorated micromolecule in biology".
Ergosterol :-It occurs in oil seed , fungi like ergot and yeast . Ergosterol is precursor of another form of Vitamin D-Ergocalciferol.
Coprosterol :-Occurs in faecal matter. It forms by decomposition of cholesterol by colon bacteria
Bile acid:- Bile Juice contains different types of steroid acids. e. g. cholic acid. Lithocholic acid etc.
They help in emulsification of fats.
(b) Sterones :- Ketonic steroids, for e. g. sex hormones, Adreno corticoids , ecdyson hormone of insects,Diosgenin obtained from yam plant (Dioscorea), is used in manufacture of antifertility pills.
(2) Chromolipid = It is also called terpene.
`->` Most complex lipid in protoplasm.
`->` Chromolipids composed of repeated isoprene units
Example : Carotenoids, vitamin `A, E, K`, Natural Hubber (Polyterpene)