Proteins
Protein name is derived from a greek word which means " holding first place" (Berzelius and Mulder)
`->` Essential elements in protein are `C , H , O, N`,
`->` Most of the proteins contain sulphur. In some proteins iodine , iron and phosphorus are present.
`->` After water, proteins are most abundant compounds in protoplasm. (`7-14%`) amount of proteins.
`->` Proteins are polymer of amino acid (Fisher and Hofmeister). There arc approximately `300` amino acids known to exist but only `20` types of amino acids are used in formation of proteins
`->` Proteins are hetero Polymer of amino acid.
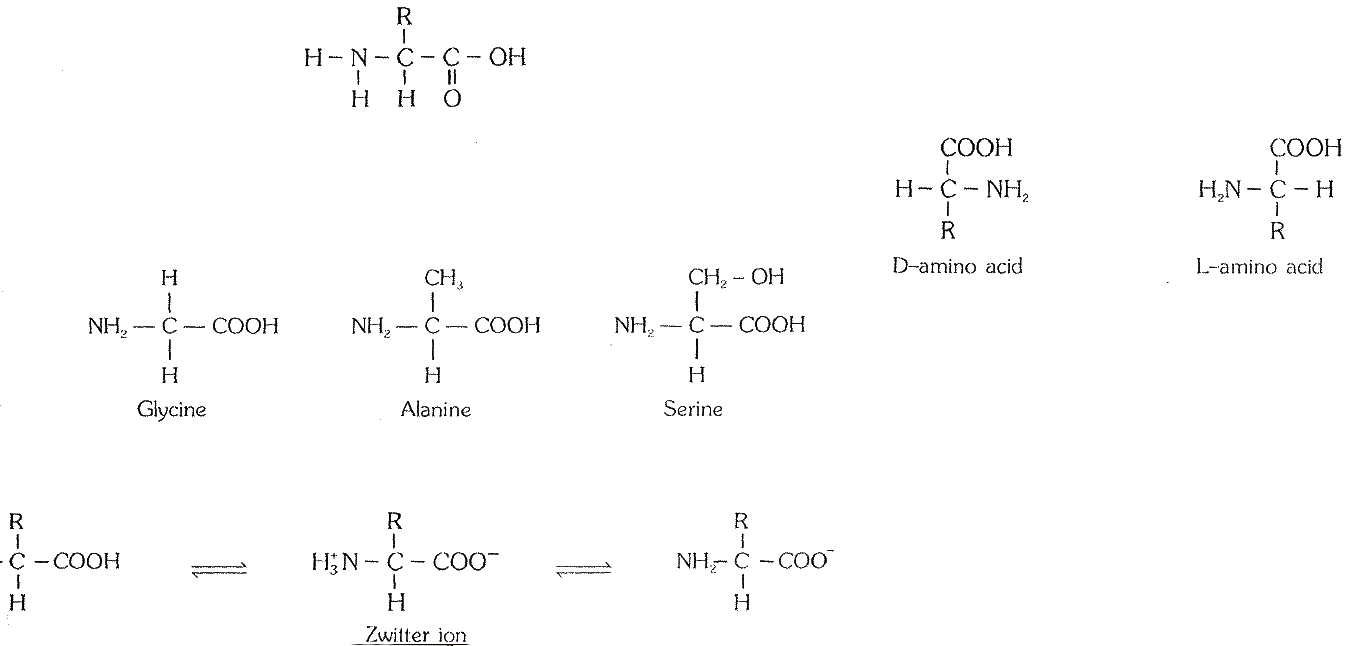
`->` Amino acids contain an amino group and carboxylic group on the same carbon i.e. the `alpha.-carbon` so they are called `alpha`-amino acid.
`->` Amino acid are substituted methane.
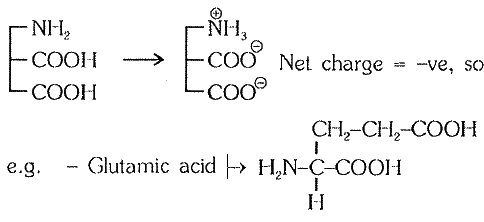
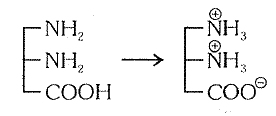
Each amino acid is amphoteric compound because it contains one acidic `-COOH` and a alkaline group `-NH_2`
`->` In protoplasm free amino acid occurs as ions (at iso electric point)
`->` Iso electric point is that point of pi I at which amino acids do not move in electric field.
`->` Out of `20` amino acids, `10` amino acids are not synthesi;ced in body of animals so they are must in diet. These
are called Essential amino acid . e. g. Threonine . Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine. Lysine, Methionine, phe-
nylalanine Tryptophan, Arginine. Histidine. Arginine and Histidine are semi essential.
`->` `10` amino acids are synthesized in animal body so these are called Non essential amino adds. for e.g.
Glycine, Alanine, Serine. Cysteinc,Aspartic acid, Clutamic acid, Asparaginc, Clutamine, Tyrosine, proline
Except glycine, each amino acid has two enantiomeric isomers
`->` Eucaryotic proteins have L- amino acid while D- amino acid occurs in bac1cria and antibodies.
`->` Essential elements in protein are `C , H , O, N`,
`->` Most of the proteins contain sulphur. In some proteins iodine , iron and phosphorus are present.
`->` After water, proteins are most abundant compounds in protoplasm. (`7-14%`) amount of proteins.
`->` Proteins are polymer of amino acid (Fisher and Hofmeister). There arc approximately `300` amino acids known to exist but only `20` types of amino acids are used in formation of proteins
`->` Proteins are hetero Polymer of amino acid.
`->` Amino acids contain an amino group and carboxylic group on the same carbon i.e. the `alpha.-carbon` so they are called `alpha`-amino acid.
`->` Amino acid are substituted methane.
Each amino acid is amphoteric compound because it contains one acidic `-COOH` and a alkaline group `-NH_2`
`->` In protoplasm free amino acid occurs as ions (at iso electric point)
`->` Iso electric point is that point of pi I at which amino acids do not move in electric field.
`->` Out of `20` amino acids, `10` amino acids are not synthesi;ced in body of animals so they are must in diet. These
are called Essential amino acid . e. g. Threonine . Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine. Lysine, Methionine, phe-
nylalanine Tryptophan, Arginine. Histidine. Arginine and Histidine are semi essential.
`->` `10` amino acids are synthesized in animal body so these are called Non essential amino adds. for e.g.
Glycine, Alanine, Serine. Cysteinc,Aspartic acid, Clutamic acid, Asparaginc, Clutamine, Tyrosine, proline
Except glycine, each amino acid has two enantiomeric isomers
`->` Eucaryotic proteins have L- amino acid while D- amino acid occurs in bac1cria and antibodies.