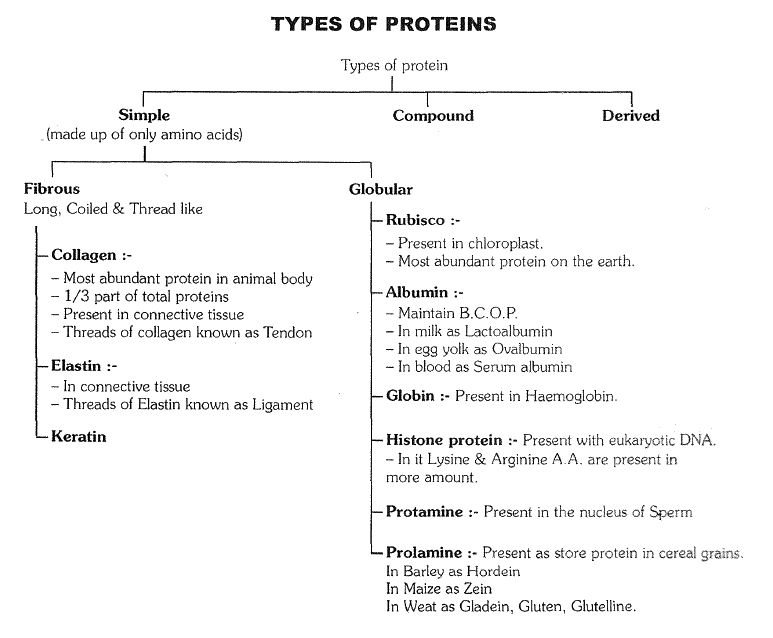
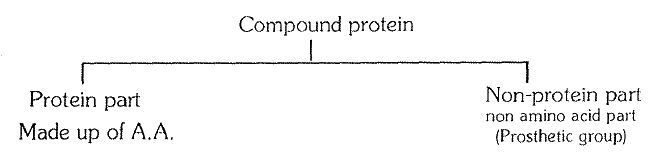
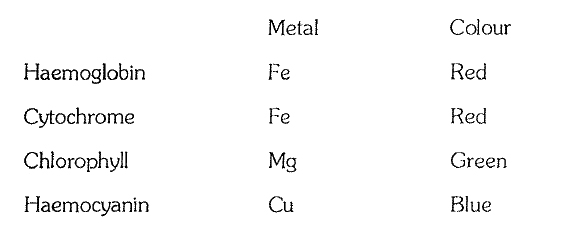`->` Besides changes in pH, salts, heavy metals, temperature, pressure, etc. also cause precipitation of proteins. Because of these changes, the secondary and tertiary configuration of proteins is destroyed. Such alternations in the physical state of proteins is called denaturation. If the change in the medium of protein is mild and for a short period, then denaturation of the protein is also temporary, however. if the change in medium is strong and prolonged then denaturation is permanent and the protein becomes coagulated. For example, the white or albumen of egg is a soluble globular protein but on heating it permanently coagulates into fibrous insoluble form. It is clear, that strong alternations result in the denaturation of proteins and they lose their biological properties and significance. It is this reason, that cells of organisms are unable to bear strong changes and they ultimately die.
`->` Besides changes in pH, salts, heavy metals, temperature, pressure, etc. also cause precipitation of proteins. Because of these changes, the secondary and tertiary configuration of proteins is destroyed. Such alternations in the physical state of proteins is called denaturation. If the change in the medium of protein is mild and for a short period, then denaturation of the protein is also temporary, however. if the change in medium is strong and prolonged then denaturation is permanent and the protein becomes coagulated. For example, the white or albumen of egg is a soluble globular protein but on heating it permanently coagulates into fibrous insoluble form. It is clear, that strong alternations result in the denaturation of proteins and they lose their biological properties and significance. It is this reason, that cells of organisms are unable to bear strong changes and they ultimately die.