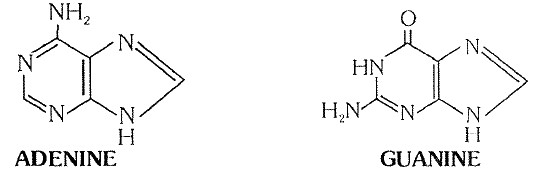Nucleic Acids
`->` F. Meischer discovered nucleic acid in nucleus of pus cell and called it "nuclein". The term nucleic acid was coined by "Altman."
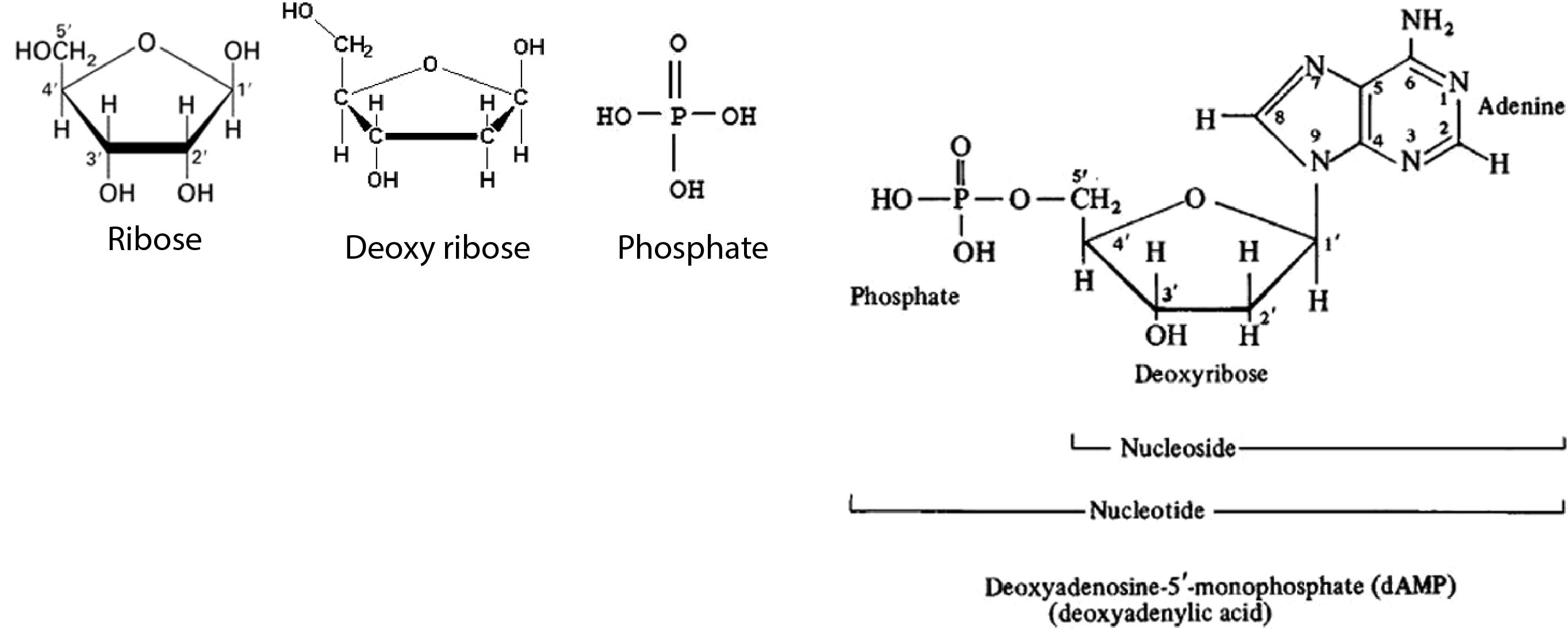
`->` Nucleic acids are polymer of nucleotides.
= Nitrogen base + pentose sugar + phosphate
On the basis of structure nitrogen bases are broadly of two types
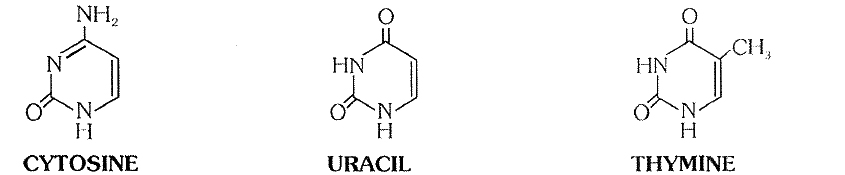
1. Pyrimidines - Consist of one pyrimidine ring. Skeleton of ring composed of two nitrogen and four Carbon
atoms. e.g. Cytosine, Thymine and Uracil.
`->` Nucleic acids are polymer of nucleotides.
= Nitrogen base + pentose sugar + phosphate
On the basis of structure nitrogen bases are broadly of two types
1. Pyrimidines - Consist of one pyrimidine ring. Skeleton of ring composed of two nitrogen and four Carbon
atoms. e.g. Cytosine, Thymine and Uracil.