Triplet Code :-
`->` The main problem of genetic code was to determine the exact number of nucleotide in a codon which codes for one amino acid.
`->` There are four types of `N_2`-bases in m-RNA `(A, U, G, C)` for `20` types of amino acids.
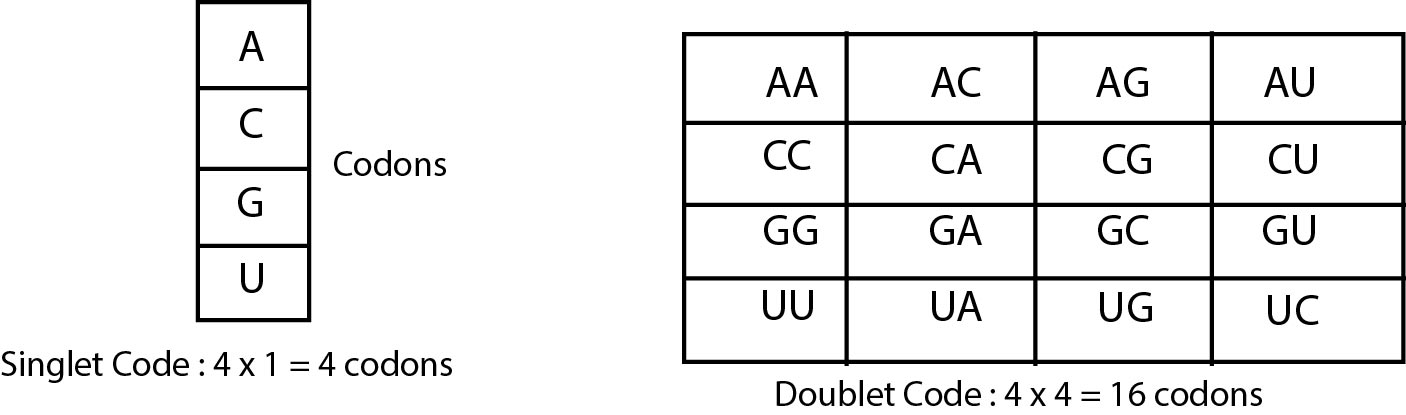
`->` If genetic code is singlet i.e. codon is the combination of only one nitrogen base, then only four codons are possible `A, C, G` and `U`. These are insufficient to code for `20` types of amino acids.
# Singlet code `= 41= 4 xx 1 = 4` codons
# If genetic code is doublet (i.e. codon is the combination of two nitrogen bases) then `16` codons are formed.
# Doublet code `= 42 = 4 xx 4 = 16` codons.
# `16` codons are insufficient for `20` amino acid
`->` Gamow (1954) pointed out the possibility of three letters code (Triplet code).
`->` Genetic code is triplet i.e. one codon consists of three nitrogen bases
Triplet code `= 43 = 4 xx 4 xx 4 = 64` codons
`->` In this case there occurs `64` codons in dictionary of genetic code.
`->` `64` codons are sufficient to code `20` types of amino acids.
`->` H.G. Khorana artificially synthesized an mRNA.
`->` Severo ochoa enzyme (RNA polymerase enzyme) is also helpful in polymerising RNA in a template independent manner.
`->` There are four types of `N_2`-bases in m-RNA `(A, U, G, C)` for `20` types of amino acids.
`->` If genetic code is singlet i.e. codon is the combination of only one nitrogen base, then only four codons are possible `A, C, G` and `U`. These are insufficient to code for `20` types of amino acids.
# Singlet code `= 41= 4 xx 1 = 4` codons
# If genetic code is doublet (i.e. codon is the combination of two nitrogen bases) then `16` codons are formed.
# Doublet code `= 42 = 4 xx 4 = 16` codons.
# `16` codons are insufficient for `20` amino acid
`->` Gamow (1954) pointed out the possibility of three letters code (Triplet code).
`->` Genetic code is triplet i.e. one codon consists of three nitrogen bases
Triplet code `= 43 = 4 xx 4 xx 4 = 64` codons
`->` In this case there occurs `64` codons in dictionary of genetic code.
`->` `64` codons are sufficient to code `20` types of amino acids.
`->` H.G. Khorana artificially synthesized an mRNA.
`->` Severo ochoa enzyme (RNA polymerase enzyme) is also helpful in polymerising RNA in a template independent manner.