Central Dogma :
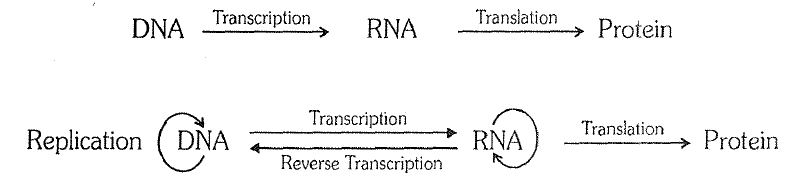
`->` Central dogma was given by Crick.
`->` The formation {production) of m- RNA from DNA and then synthesis of protein from it, is known as Central Dogma.
`->` It means, it includes transcription and translation.
`->` The formation {production) of m- RNA from DNA and then synthesis of protein from it, is known as Central Dogma.
`->` It means, it includes transcription and translation.