Conservation of Linear Momentum
It states that,
''In an isolated system (no external force), the algebraic some of the momenta of bodies, along any straight line, remains constant and is not changed due to their mutual action and reaction on each other.''
This can be verified by a following simple experiment.
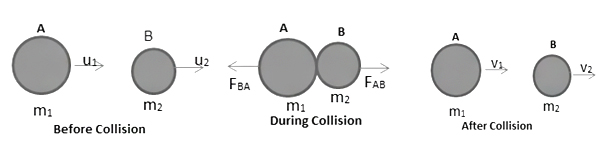
Consider a body A of mass `m_1` moving with a velocity `vec{u_{1}}` strike against another body `B` of mass `m_2`,moving with velocity `vecu_2` in same direction as shown in the below figure. Two bodies remain in contact with each other for small time, Then they get separated after collision and move with velocities`vec{v_{1}} ` and `vec{v_{2}}`.
By conservation of Linear Momentum
Initial linear momentum = final linear momentum
`m_1u_1+m_2u_2 = m_1v_1+m_2v_2`
''In an isolated system (no external force), the algebraic some of the momenta of bodies, along any straight line, remains constant and is not changed due to their mutual action and reaction on each other.''
This can be verified by a following simple experiment.
Consider a body A of mass `m_1` moving with a velocity `vec{u_{1}}` strike against another body `B` of mass `m_2`,moving with velocity `vecu_2` in same direction as shown in the below figure. Two bodies remain in contact with each other for small time, Then they get separated after collision and move with velocities`vec{v_{1}} ` and `vec{v_{2}}`.
By conservation of Linear Momentum
Initial linear momentum = final linear momentum
`m_1u_1+m_2u_2 = m_1v_1+m_2v_2`