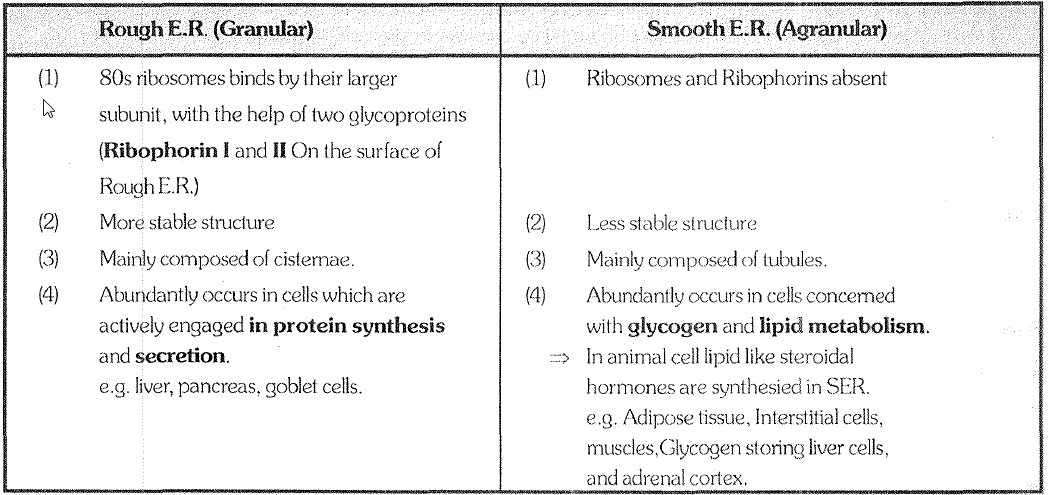
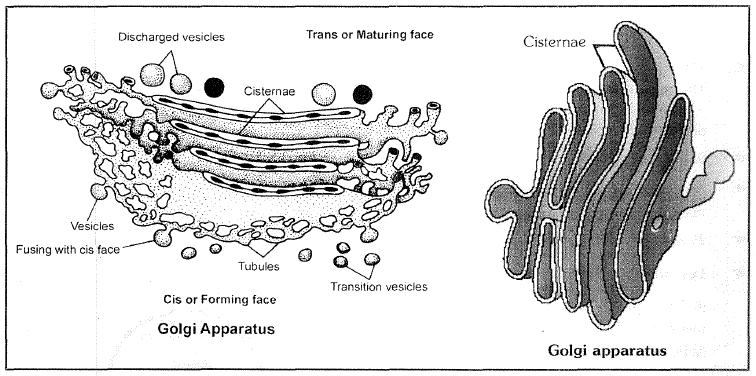
Endomembrane System :
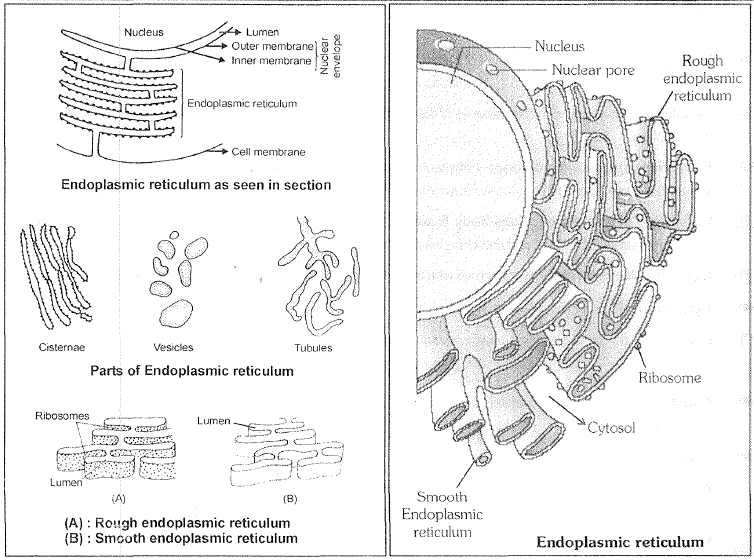
`->` While each of the membranous organelles is distinct in terms of its structure and function. many of these are considered together as an endomembrane system because their functions are coordinated.
`->` The endomembrance system include endoplasmic reticulum (ER), golgi complex, lysosomes and vacuoles. Since the functions of the mitochondria, choroplast and peroxisomes are not coordinated with the above components, these are not considered as part of the endornembrane system.
`->` The endomembrance system include endoplasmic reticulum (ER), golgi complex, lysosomes and vacuoles. Since the functions of the mitochondria, choroplast and peroxisomes are not coordinated with the above components, these are not considered as part of the endornembrane system.