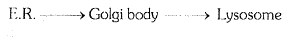Lysosome :
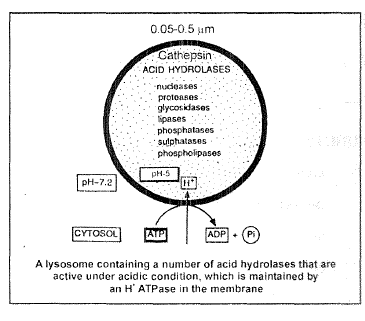
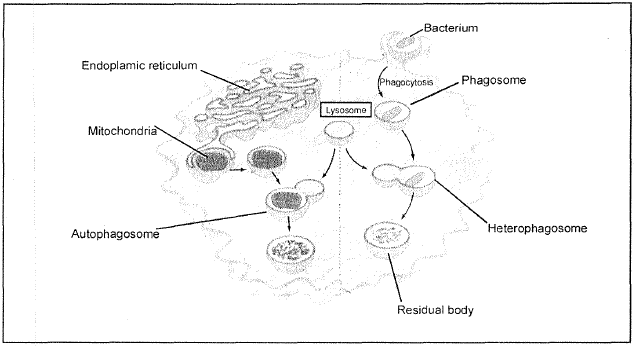
`->` These are membrane bound vesicular structures formed by the process of packaging in the golgi apparatus. The isolated lysosomal vesicles have been found to be very rich in almost all types of hydrolytic enzymes (hydrolases -lipases, proteases, carbohydrases) optimally active at the acidic pH (`pH = 5`). These enzymes are capable of digesting carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.
`->` With the exception of mammalian RBC they were reported from all cells.
`->` In plant cells large central vacuole functions as Lysosome. So in higher plants lysosomes are less frequent. But number of lysosomes is high in fungi.
`->` Periplasmic Space:- space between cell wall and cell membrane in bacteria, may play similar role.
`->` Lysosomes are spherical bag like structures (`0.1-0.8 mu` m) which is covered by single unit membrane. They are large sized in Phagocytes (WBC) (`0.8` to `2 mu` m).
`->` Lysosomes are filled with `50` different type of digestive enzymes termed as Acid hydrolases.
These acid hydrolases function in acidic medium(` pH = 5`).Membrane of lysosome has an active `H^+` pump mechanism which produce acidic pH in lumen of lysosome.
`->` Lysosomes are highly polymorphic cell organelle. Because, during functioning, lysosomes have different morphological and physiological states.
`->` With the exception of mammalian RBC they were reported from all cells.
`->` In plant cells large central vacuole functions as Lysosome. So in higher plants lysosomes are less frequent. But number of lysosomes is high in fungi.
`->` Periplasmic Space:- space between cell wall and cell membrane in bacteria, may play similar role.
`->` Lysosomes are spherical bag like structures (`0.1-0.8 mu` m) which is covered by single unit membrane. They are large sized in Phagocytes (WBC) (`0.8` to `2 mu` m).
`->` Lysosomes are filled with `50` different type of digestive enzymes termed as Acid hydrolases.
These acid hydrolases function in acidic medium(` pH = 5`).Membrane of lysosome has an active `H^+` pump mechanism which produce acidic pH in lumen of lysosome.
`->` Lysosomes are highly polymorphic cell organelle. Because, during functioning, lysosomes have different morphological and physiological states.