Chemical Composition of Ribosomes :
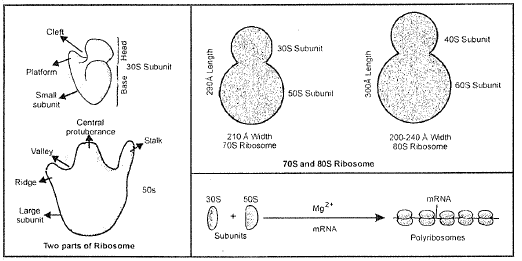
`70`s - `60%` r- RNA + `40%` proteins
`80`s - `40%` r-RNA + `60%` proteins
`60`s - r-RNA `28`s, `5.8`s, `5`s
`40`s - r-RNA `18`s
`50`s - r-RNA `23`s,`5`s
`30`s - r-RNA `16`s
`->` At the time of protein synthesis, several ribosomes become attached to m-RNA with the help of smaller subunits. This structure is called polyribosome or polysome or Ergosome. Ribosomes move along the m-RNA like beads on a string, during protein synthesis. Larger subunit contains peptidyl transferase enzyme (`23`s rRNA) which helps in the formation of peptide bond during protein synthesis. This is an example of Ribozyme. (Noller 1992)
Two sites are found on larger sub units :
(i) A- site -->Acceptor site for l-ENA
(ii) P-site --> site for growing polypeptide chain
After synthesis on ribosomes, protein are transported in cytoplasm and organelles.
The proper folding and transport of proteins is assisted by specific proteins called Chaperons.
`80`s - `40%` r-RNA + `60%` proteins
`60`s - r-RNA `28`s, `5.8`s, `5`s
`40`s - r-RNA `18`s
`50`s - r-RNA `23`s,`5`s
`30`s - r-RNA `16`s
`->` At the time of protein synthesis, several ribosomes become attached to m-RNA with the help of smaller subunits. This structure is called polyribosome or polysome or Ergosome. Ribosomes move along the m-RNA like beads on a string, during protein synthesis. Larger subunit contains peptidyl transferase enzyme (`23`s rRNA) which helps in the formation of peptide bond during protein synthesis. This is an example of Ribozyme. (Noller 1992)
Two sites are found on larger sub units :
(i) A- site -->Acceptor site for l-ENA
(ii) P-site --> site for growing polypeptide chain
After synthesis on ribosomes, protein are transported in cytoplasm and organelles.
The proper folding and transport of proteins is assisted by specific proteins called Chaperons.