SOLUTION OF DIFFRENTIAL EQUATIONS BY THE METHOD OF SEPARATION OF VARIABLES
Solution Of a differential equation :
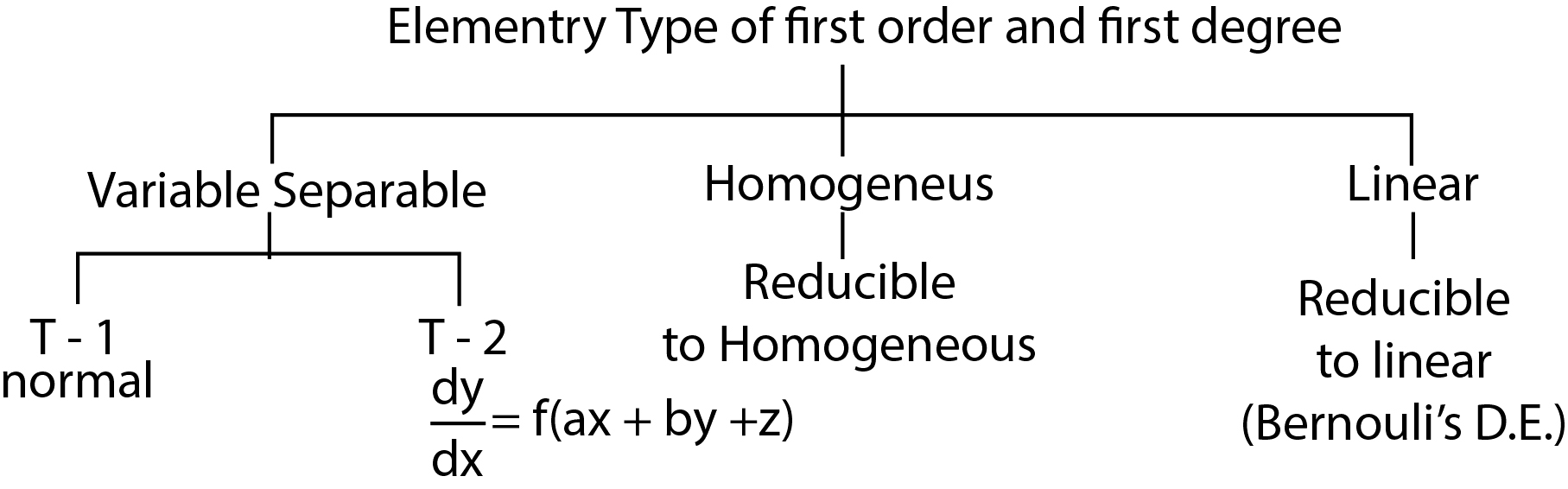
`text( T-1. Variables Separable :) `
If the differential equation can be expressed as; `f(x)dx + g(y)dy = 0` then this is said to be variable -separable type.
A general solution of this is given by `int f(x) dx + int g(y) dy =c`; where c is the arbitrary constant.
`text( T-2. Differential Equation Reducible to the Separable Variable Type:)`
`dy /dx = f (ax +by +c), a,b ne 0`
To solve this , substitute `t = ax+ by + c`. Then the equation reduces to separable type in the
variable `t` and `x` which can be solved.
`text( T-1. Variables Separable :) `
If the differential equation can be expressed as; `f(x)dx + g(y)dy = 0` then this is said to be variable -separable type.
A general solution of this is given by `int f(x) dx + int g(y) dy =c`; where c is the arbitrary constant.
`text( T-2. Differential Equation Reducible to the Separable Variable Type:)`
`dy /dx = f (ax +by +c), a,b ne 0`
To solve this , substitute `t = ax+ by + c`. Then the equation reduces to separable type in the
variable `t` and `x` which can be solved.