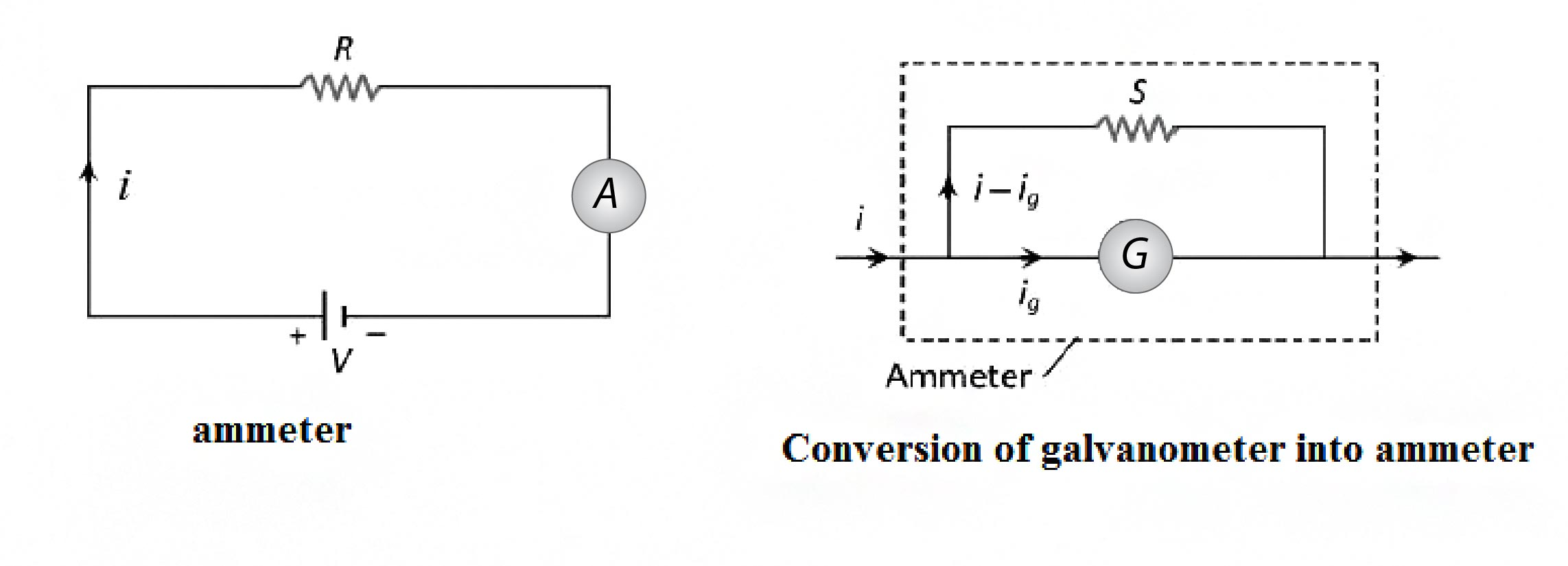
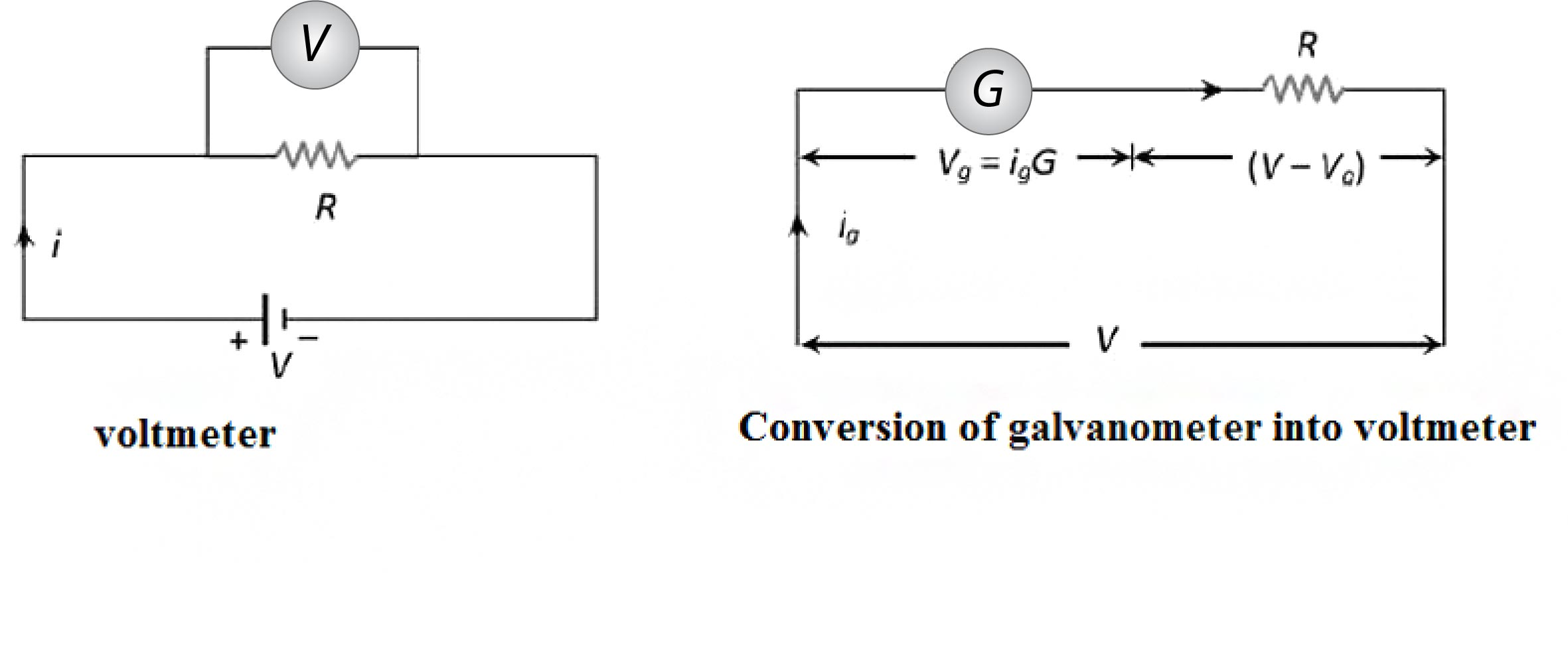
Galvanometer

It is an instrument used to detect small current passing through it by showing deflection. Galvanometers
are of different types e.g. moving coil galvanometer, moving magnet galvanometer, hot wire galvanometer.
In DC circuit usually moving coiI galvanometer are used.
(i) Full scale deflection current: The current required for full scale deflection in a galvanometer is called
full scale deflection current and is represented by `i_g`,
(ii) Shunt : The small resistance connected in parallel to galvanometer coil, in order to control current
flowing through the galvanometer is known as shunt.
are of different types e.g. moving coil galvanometer, moving magnet galvanometer, hot wire galvanometer.
In DC circuit usually moving coiI galvanometer are used.
(i) Full scale deflection current: The current required for full scale deflection in a galvanometer is called
full scale deflection current and is represented by `i_g`,
(ii) Shunt : The small resistance connected in parallel to galvanometer coil, in order to control current
flowing through the galvanometer is known as shunt.