Electrice cell or Battery
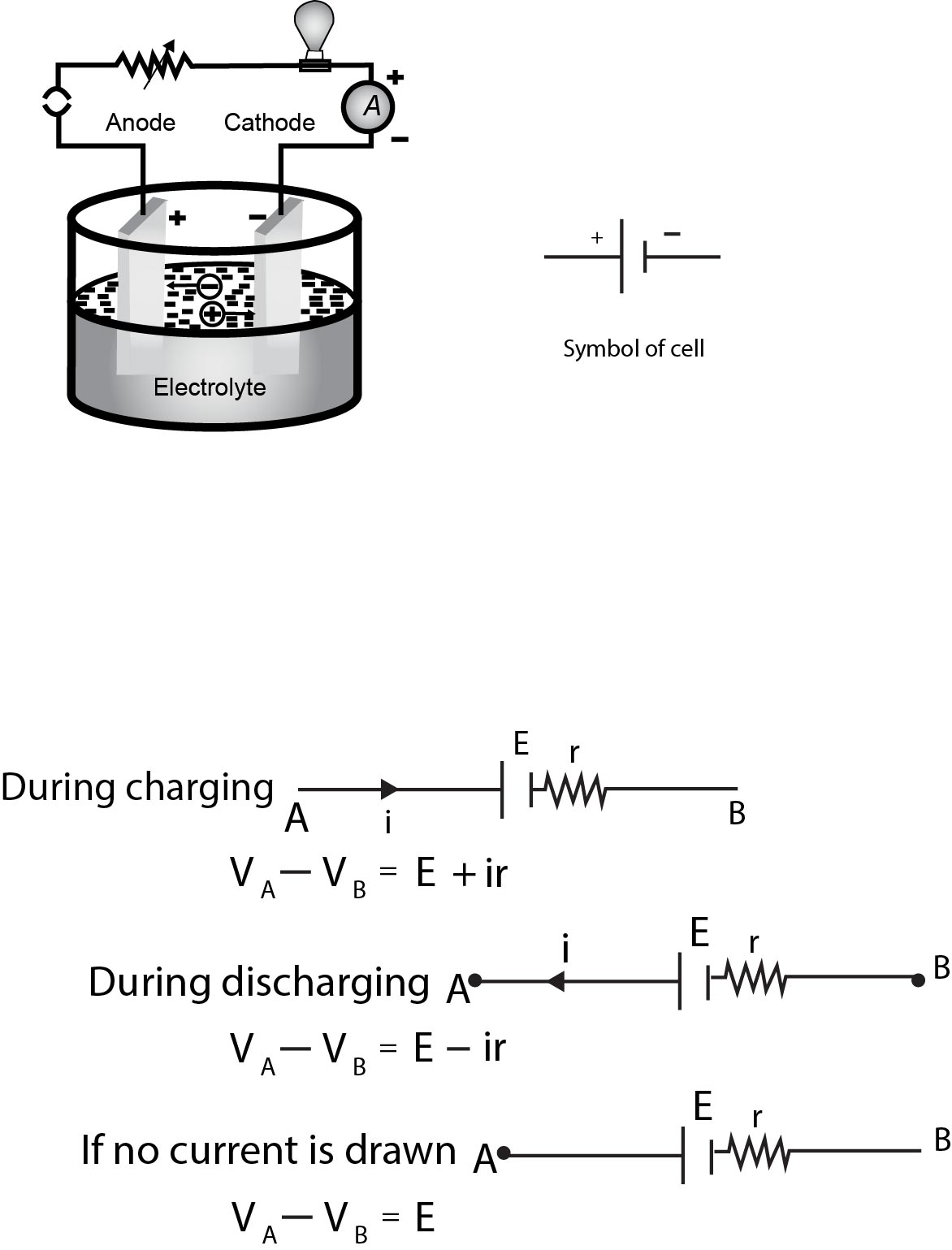
Cell is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy and also electrical energy into chemical .Cell is a
source of constant emf but not constant current.
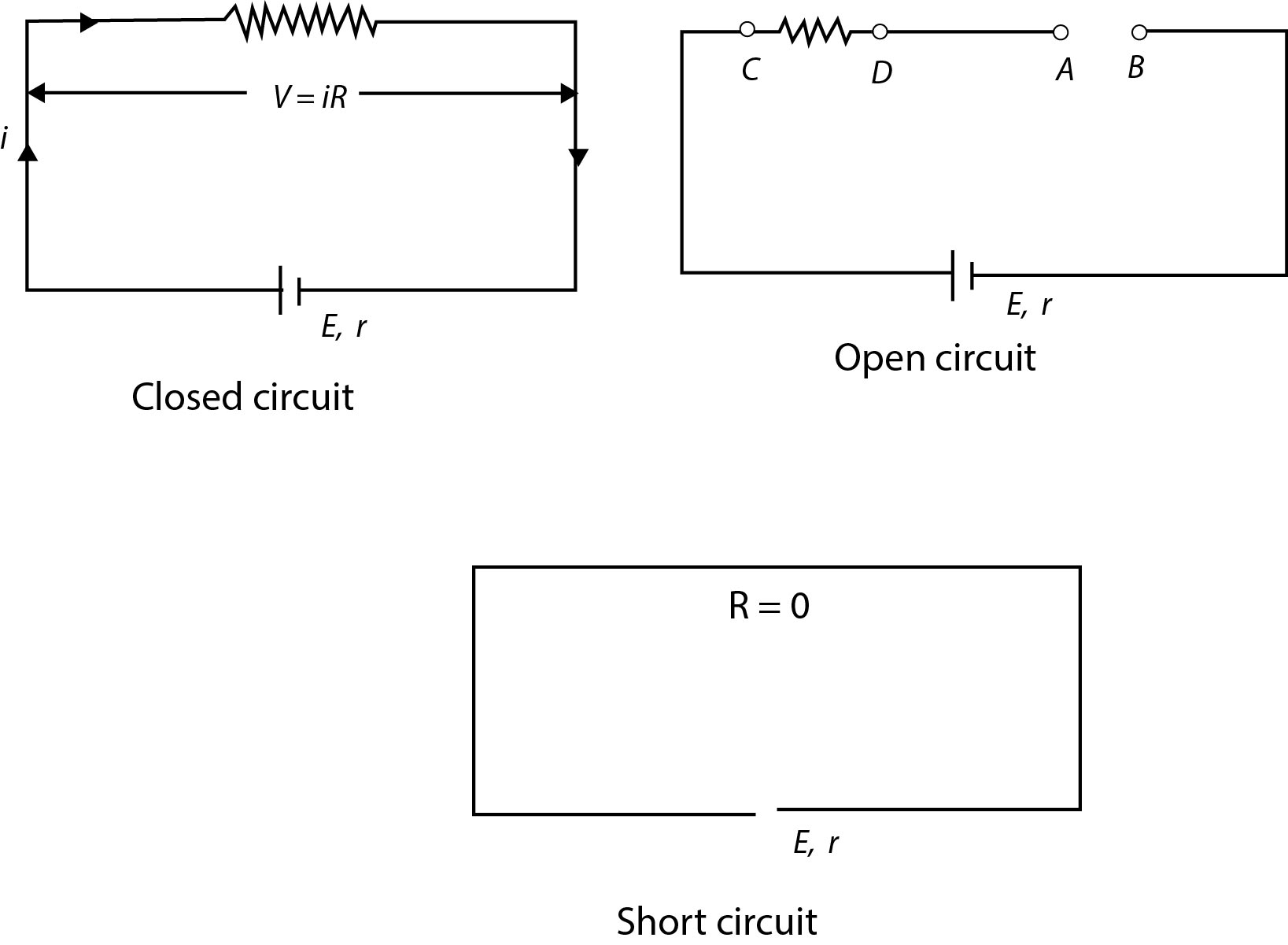
`text( Emf of cell)` (E): The potential difference across the tenninals of a cell when it is not supplying any
current (open circuit ) is called it's emf.
`text( Potential difference)` (V) : The voltage across the terminals of a cell when it is supplying current to
external resistance is called potential difference or terminal voltage.
When cell discharges, its terminal potential is less than its Emf and in this chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
When cell is being charge its terminal potential is more than its Emf and in this electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
`text( Internal resistance )`(r) : In case of a cell the opposition of electrolyte to the flow of current through it
is called internal resistance of the cell. The internal resistance of a cell depends on the distance between
electrodes `(r prop d)`. area of electrodes `[r prop 1/A]` and nature, concentration `(r prop C)` and temperature of
electrolyte `[r prop( 1/text(temp)))`
`text(A cell is said to be ideal, if it has zero internal resistance.)`
source of constant emf but not constant current.
`text( Emf of cell)` (E): The potential difference across the tenninals of a cell when it is not supplying any
current (open circuit ) is called it's emf.
`text( Potential difference)` (V) : The voltage across the terminals of a cell when it is supplying current to
external resistance is called potential difference or terminal voltage.
When cell discharges, its terminal potential is less than its Emf and in this chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
When cell is being charge its terminal potential is more than its Emf and in this electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
`text( Internal resistance )`(r) : In case of a cell the opposition of electrolyte to the flow of current through it
is called internal resistance of the cell. The internal resistance of a cell depends on the distance between
electrodes `(r prop d)`. area of electrodes `[r prop 1/A]` and nature, concentration `(r prop C)` and temperature of
electrolyte `[r prop( 1/text(temp)))`
`text(A cell is said to be ideal, if it has zero internal resistance.)`