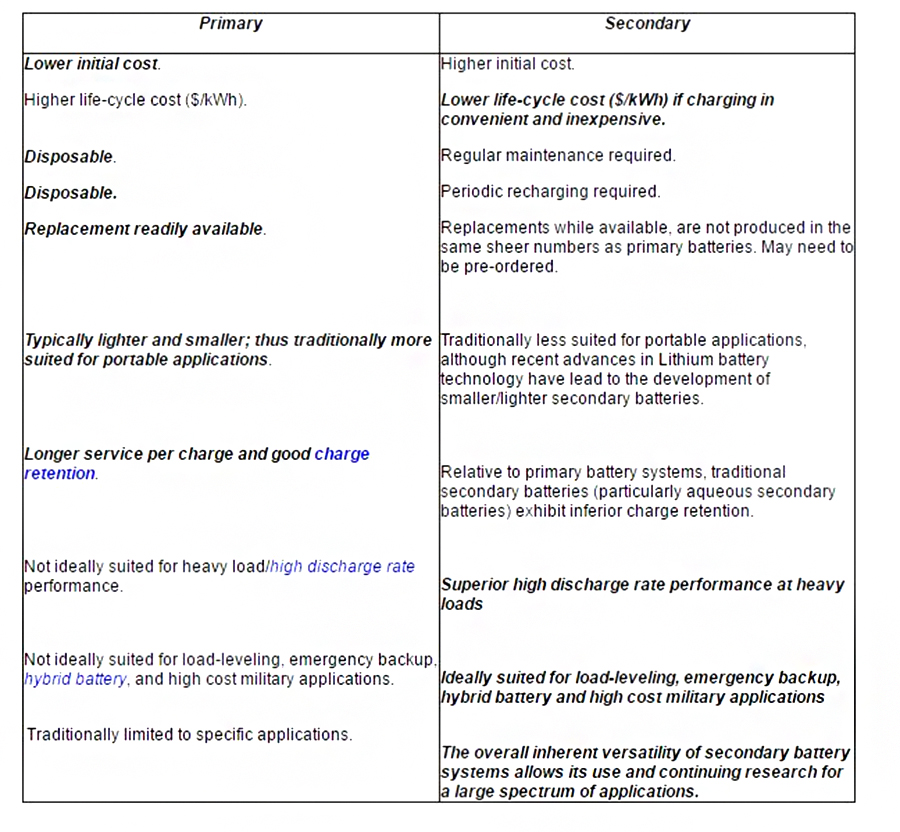
secondary cell or battery
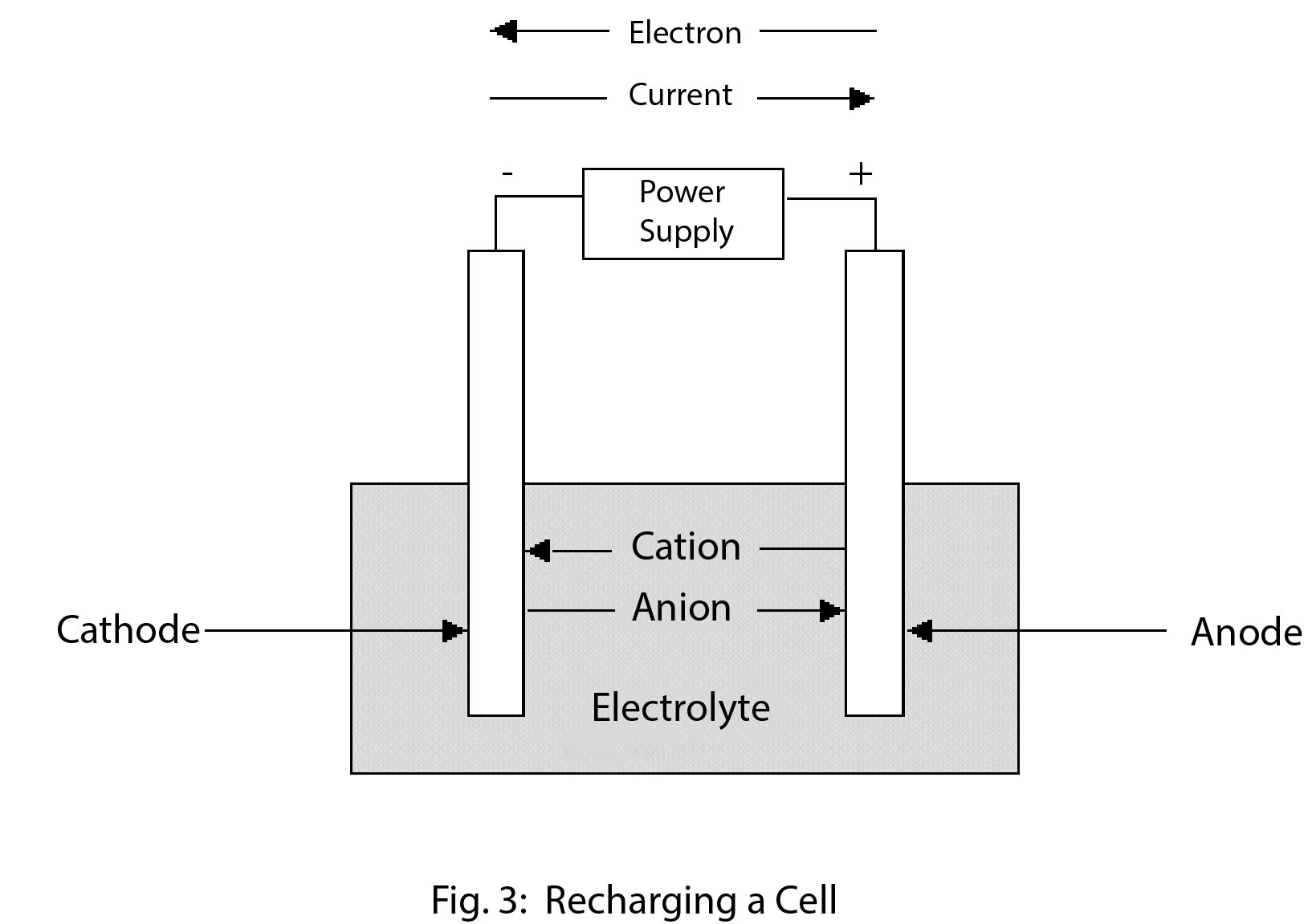
A secondary cell or battery is one that can be electrically recharged after use to their original pre-discharge condition, by passing current through the circuit in the opposite direction to the current during discharge. The following graphic evidences the recharging process.
Secondary batteries fall into two sub-categories depending on their intended applications.
(i)Cells that are utilized as energy storage devices, delivering energy on demand. Such cells are typically connected to primary power sources so as to be fully charged on demand. Examples of these type of secondary cells include emergency no-fail and standby power sources, aircraft systems and stationary energy storage systems for load-leveling.
(ii)Cells that are essentially utilized as primary cells, but are recharged after use rather than being discarded. Examples of these types of secondary cells primarily include portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles.
ie Chemical reaction involved is bidirectional
Secondary batteries fall into two sub-categories depending on their intended applications.
(i)Cells that are utilized as energy storage devices, delivering energy on demand. Such cells are typically connected to primary power sources so as to be fully charged on demand. Examples of these type of secondary cells include emergency no-fail and standby power sources, aircraft systems and stationary energy storage systems for load-leveling.
(ii)Cells that are essentially utilized as primary cells, but are recharged after use rather than being discarded. Examples of these types of secondary cells primarily include portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles.
ie Chemical reaction involved is bidirectional