Magnetic Properties :
`ast` Matter, in general is associated with magnetic properties. Majority of substances are either paramagnetic or diamagnetic. A paramagnetic substance is one which is attracted into a magnetic field. Paramagnetism is mainly due to the presence of unpaired electrons in atoms or ions or molecules. Diamagnetic substance is one which is slightly repelled by a magnetic field.
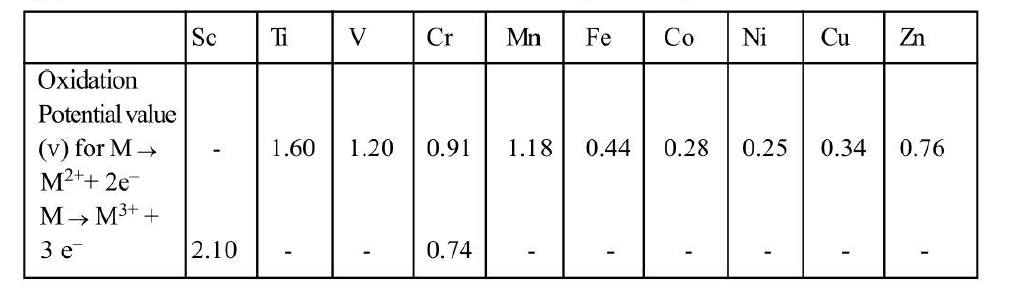
`ast` `Ti^(+2) [Ar]3d^2`, `Ti^(+3) [Ar]3d^1`, `V^(+2)[Ar]3d^3`, `Cr^(+1) [Ar]3d^3`
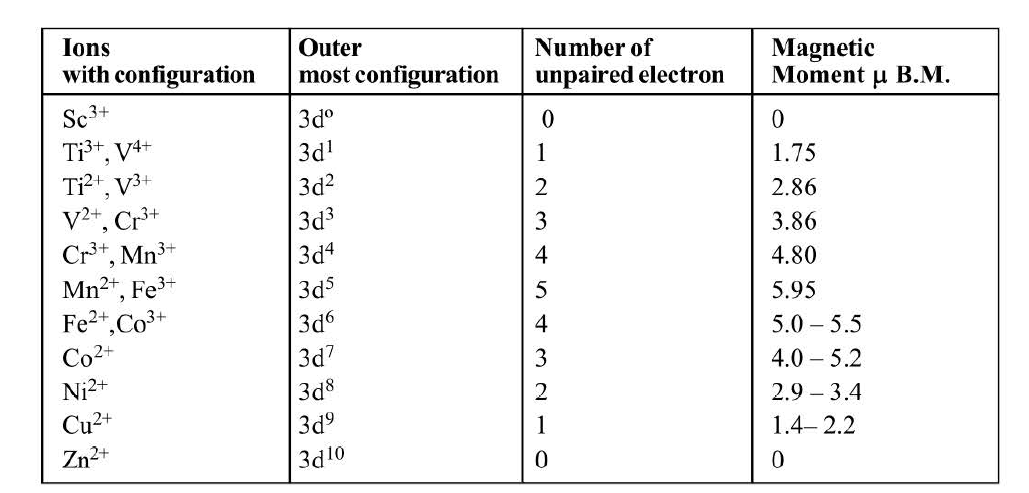
As is evident most of the transition metal ions have unpaired electrons in their `d` orbitals. Hence most of the transition metal ions are paramagnetic in nature. Transition metal ions having `3d^0` and `3d^10` configuration exhibit diamagnetic nature.
`ast` An unpaired electron spins and as it is a charged particle, magnetic field is created due to its spinning.
`ast` Each electron may, in fact, be considered as a micro magnet having a certain value of magnetic moment. The total magnetic moment of a substance is the resultant of the magnetic moments of all the individual electrons. Thus substances containing unpaired electrons get attracted towards the magnets exhibiting paramagnetic nature.
`ast` The magnetic moment `(mu)` created due to spinning of unpaired electrons can be calculated by using
`mu = sqrt[n(n + 2)]` : Where `n` is the number of unpaired electrons in the metal ion.
`mu =` Magnetic moment in Bohr Magnetons (B.M.)
`ast` The magnetic moment of diamagnetic substances will be zero.
`ast` As the number of unpaired electrons increase the magnetic moment created goes on increasing and hence the paramagnetic nature also increases.
`ast` Transition metal ions having `d^5` configuration will have maximum number of unpaired electrons therefore they will be maximum paramagnetic in nature.
Variation of Magnetic moment of `3d`-series : See table.
`ast` `Ti^(+2) [Ar]3d^2`, `Ti^(+3) [Ar]3d^1`, `V^(+2)[Ar]3d^3`, `Cr^(+1) [Ar]3d^3`
As is evident most of the transition metal ions have unpaired electrons in their `d` orbitals. Hence most of the transition metal ions are paramagnetic in nature. Transition metal ions having `3d^0` and `3d^10` configuration exhibit diamagnetic nature.
`ast` An unpaired electron spins and as it is a charged particle, magnetic field is created due to its spinning.
`ast` Each electron may, in fact, be considered as a micro magnet having a certain value of magnetic moment. The total magnetic moment of a substance is the resultant of the magnetic moments of all the individual electrons. Thus substances containing unpaired electrons get attracted towards the magnets exhibiting paramagnetic nature.
`ast` The magnetic moment `(mu)` created due to spinning of unpaired electrons can be calculated by using
`mu = sqrt[n(n + 2)]` : Where `n` is the number of unpaired electrons in the metal ion.
`mu =` Magnetic moment in Bohr Magnetons (B.M.)
`ast` The magnetic moment of diamagnetic substances will be zero.
`ast` As the number of unpaired electrons increase the magnetic moment created goes on increasing and hence the paramagnetic nature also increases.
`ast` Transition metal ions having `d^5` configuration will have maximum number of unpaired electrons therefore they will be maximum paramagnetic in nature.
Variation of Magnetic moment of `3d`-series : See table.