The essence of first law is that all physical and chemical processes take place in such a manner that the total energy of the universe remain constant.
However, it is observed that all processes have a natural direction,i.e. a direction in which they take place spontaneously. First law fails to answer this. Another feature of the spontaneous processes is that they proceed only until an equilibrium is achieved. The direction of a spontaneous process and that it eventually reaches equilibrium, can be understood on the basis of entropy concept introduced through
the second law of thermodynamics.
`text(The second law can be expressed in alternative forms as below)` :
(A) `text(Clausius statement)` : Clausius is credited with the first formulation of the second law, now known as the Clausius statement.
`text(No process is possible whose sole result is the transfer of heat from a body of lower temperature to a body of higher temperature)`.
Spontaneously, heat cannot flow from cold regions to hot regions without external work being performed on the system, which is evident from ordinary experience of refrigeration, for example. In a refrigerator, heat flows from cold to hot, but only when forced by an external agent, a compressor.
(B) `text(Kelvin statement)` : The Kelvin statement expressed the second law in another form:
`text(No process is possible in which the sole result is the absorption of heat from a reservoir and its Complete conversion into work.)`
This means it is impossible to extract energy by heat from a high-temperature energy source and then convert all of the energy into work. At least some of the energy must be passed on to heat a low temperature energy sink. Thus, a heat engine with `100%` efficiency is thermodynamically impossible.
This also means that it is impossible to build solar panels that generate electricity solely from the infrared band of the electromagnetic spectrum without consideration of the temperature on the other side of the panel (as is the case with conventional solar panels that operate in the visible spectrum). Note that it is possible to convert heat completely into work, such as the isothermal expansion of ideal
gas. However, such a process has an additional result. In the case of the isothermal expansion, the volume of the gas increases and never goes back without outside interference.
`text(Corollaries)` :
(A) `text(Perpetual motion of the second kind)`
Prior to the establishment of the Second Law, many people who were interested in inventing a perpetual motion machine had tried to circumvent the restrictions of First Law of Thermodynamics by extracting the massive internal energy of the environment as the power of the machine. Such a machine is called a "perpetual motion machine of the second kind". The second law declared the impossibility of such machines.
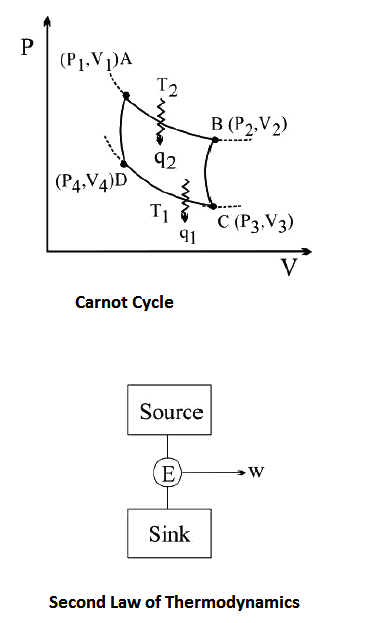
(B) `text(Carnot theorem)`
Carnot's theorem is a principle that limits the maximum efficiency for any possible engine. The efficiency solely depends on the temperature difference between the hot and cold thermal reservoirs. Carnot's theorem states:
`ast` All irreversible heat engines between two heat reservoirs are less efficient than a Carnot engine operating between the same reservoirs.
`ast` All reversible heat engines between two heat reservoirs are equally efficient with a Carnot engine operating between the same reservoirs.
The essence of first law is that all physical and chemical processes take place in such a manner that the total energy of the universe remain constant.
However, it is observed that all processes have a natural direction,i.e. a direction in which they take place spontaneously. First law fails to answer this. Another feature of the spontaneous processes is that they proceed only until an equilibrium is achieved. The direction of a spontaneous process and that it eventually reaches equilibrium, can be understood on the basis of entropy concept introduced through
the second law of thermodynamics.
`text(The second law can be expressed in alternative forms as below)` :
(A) `text(Clausius statement)` : Clausius is credited with the first formulation of the second law, now known as the Clausius statement.
`text(No process is possible whose sole result is the transfer of heat from a body of lower temperature to a body of higher temperature)`.
Spontaneously, heat cannot flow from cold regions to hot regions without external work being performed on the system, which is evident from ordinary experience of refrigeration, for example. In a refrigerator, heat flows from cold to hot, but only when forced by an external agent, a compressor.
(B) `text(Kelvin statement)` : The Kelvin statement expressed the second law in another form:
`text(No process is possible in which the sole result is the absorption of heat from a reservoir and its Complete conversion into work.)`
This means it is impossible to extract energy by heat from a high-temperature energy source and then convert all of the energy into work. At least some of the energy must be passed on to heat a low temperature energy sink. Thus, a heat engine with `100%` efficiency is thermodynamically impossible.
This also means that it is impossible to build solar panels that generate electricity solely from the infrared band of the electromagnetic spectrum without consideration of the temperature on the other side of the panel (as is the case with conventional solar panels that operate in the visible spectrum). Note that it is possible to convert heat completely into work, such as the isothermal expansion of ideal
gas. However, such a process has an additional result. In the case of the isothermal expansion, the volume of the gas increases and never goes back without outside interference.
`text(Corollaries)` :
(A) `text(Perpetual motion of the second kind)`
Prior to the establishment of the Second Law, many people who were interested in inventing a perpetual motion machine had tried to circumvent the restrictions of First Law of Thermodynamics by extracting the massive internal energy of the environment as the power of the machine. Such a machine is called a "perpetual motion machine of the second kind". The second law declared the impossibility of such machines.
(B) `text(Carnot theorem)`
Carnot's theorem is a principle that limits the maximum efficiency for any possible engine. The efficiency solely depends on the temperature difference between the hot and cold thermal reservoirs. Carnot's theorem states:
`ast` All irreversible heat engines between two heat reservoirs are less efficient than a Carnot engine operating between the same reservoirs.
`ast` All reversible heat engines between two heat reservoirs are equally efficient with a Carnot engine operating between the same reservoirs.