Exponential Function
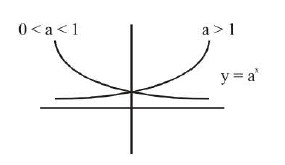
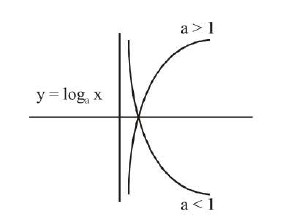
A function `f(x) = a^x = e^(xlna) (a > O , a!=1, , x in R)` is called an exponential function. `f(x) = a^x` is called an exponential function
because the variable xis the exponent. It should not be confused with power function. `g (x) = x^2` in which variable xis the base.
For `f(x) = e^x ` domain is `R` and range is `R^+`.
For `f(x) = e^(1/x)` domain is `R- {0}` and range is `R^+ - {1}. i.e (0,1) uu(1,oo)`
`f(x) = 1/(ln x)` with domain `R^+ -{1}`, range is `R- {0}`
because the variable xis the exponent. It should not be confused with power function. `g (x) = x^2` in which variable xis the base.
For `f(x) = e^x ` domain is `R` and range is `R^+`.
For `f(x) = e^(1/x)` domain is `R- {0}` and range is `R^+ - {1}. i.e (0,1) uu(1,oo)`
`f(x) = 1/(ln x)` with domain `R^+ -{1}`, range is `R- {0}`