Silicones :
It is organo silicon polymer.
`C Cl_4 + H_2O rightarrow text(no hydrolysis)`
but `C Cl_4 + undersettext(super heated)(H_2O) rightarrow COCl_2+2HCl`
`SiCl_4 + H_2 oversettext(steam) rightarrow Si(OH)_4+4HCl`
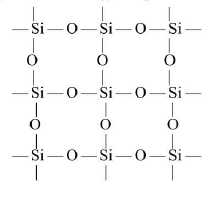
`Si(OH)_4 underset(-2H_2O) overset(Delta) rightarrow SiO_2 text(3-D silicate)`
`R_2SiCl_2 + H_2O underset(-2HCl) rightarrow R_2Si(OH)_2 underset(H_2O) overset(Delta) rightarrow undersettext(Linear silicone)(-O-R_2Si-O-R_2Si-O-R_2Si-O)`
`R_2C Cl_2 + H_2O undersettext[-2HCl text(looses) H_2O text(readily)] rightarrow R_2C(OH)_2 overset(-H_2O) rightarrow (R-C=O-R)`
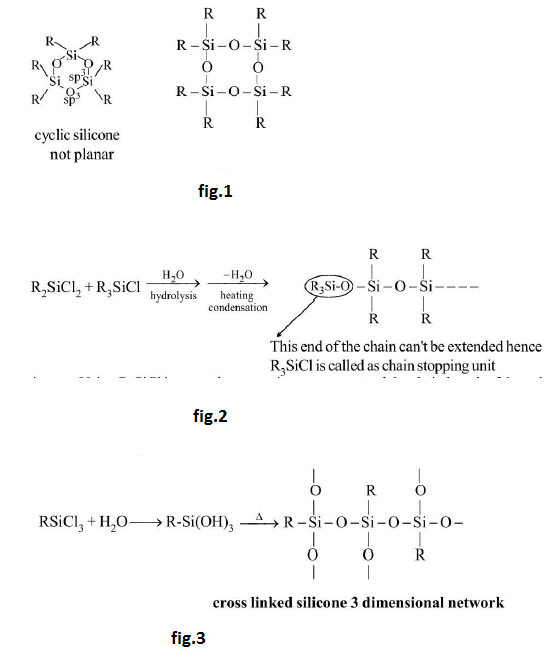
Silicones may have the cyclic structure also having `3`, `4`, `5` and `6` numbers of silicon atoms within the ring. Alcohol analogue of silicon is known as silanol. See fig.1.
`R_3SiCl overset(H_2O) rightarrow undersettext(silanol)(R_3SiOH) underset(Delta) overset(-H_2O) rightarrow R_3Si-O-SiR_3`
`R_2SiCl_2 + R_3SiCl undersettext(hydrolysis) overset(H_2O) rightarrow undersettext(heating condensation) overset(-H_2O) rightarrow R_3Si-O-R_2Si-O-R_2Si--`
See fig.2.
Using `R_3SiCl` in a certain proportion we can control the chain length of the polymer.
See fig.3.
It provides the crosslinking among the chain making the polymer more hard and hence controlling the proportion of `RSiCl_3` we can control the hardness of polymer.
Uses :
(i) It can be used as electrical insulator (due to inertness of `Si-O- Si` bonds).
(ii) It is used as water repellant (because surface is covered) eg. car polish, shoe polish, massonary works in buildings.
(iii) It is used as anti foaming agent in sewage disposal, beer making and in cooking oil used to prepare potato chips.
(iv) As a lubricant in the gearboxes.
`C Cl_4 + H_2O rightarrow text(no hydrolysis)`
but `C Cl_4 + undersettext(super heated)(H_2O) rightarrow COCl_2+2HCl`
`SiCl_4 + H_2 oversettext(steam) rightarrow Si(OH)_4+4HCl`
`Si(OH)_4 underset(-2H_2O) overset(Delta) rightarrow SiO_2 text(3-D silicate)`
`R_2SiCl_2 + H_2O underset(-2HCl) rightarrow R_2Si(OH)_2 underset(H_2O) overset(Delta) rightarrow undersettext(Linear silicone)(-O-R_2Si-O-R_2Si-O-R_2Si-O)`
`R_2C Cl_2 + H_2O undersettext[-2HCl text(looses) H_2O text(readily)] rightarrow R_2C(OH)_2 overset(-H_2O) rightarrow (R-C=O-R)`
Silicones may have the cyclic structure also having `3`, `4`, `5` and `6` numbers of silicon atoms within the ring. Alcohol analogue of silicon is known as silanol. See fig.1.
`R_3SiCl overset(H_2O) rightarrow undersettext(silanol)(R_3SiOH) underset(Delta) overset(-H_2O) rightarrow R_3Si-O-SiR_3`
`R_2SiCl_2 + R_3SiCl undersettext(hydrolysis) overset(H_2O) rightarrow undersettext(heating condensation) overset(-H_2O) rightarrow R_3Si-O-R_2Si-O-R_2Si--`
See fig.2.
Using `R_3SiCl` in a certain proportion we can control the chain length of the polymer.
See fig.3.
It provides the crosslinking among the chain making the polymer more hard and hence controlling the proportion of `RSiCl_3` we can control the hardness of polymer.
Uses :
(i) It can be used as electrical insulator (due to inertness of `Si-O- Si` bonds).
(ii) It is used as water repellant (because surface is covered) eg. car polish, shoe polish, massonary works in buildings.
(iii) It is used as anti foaming agent in sewage disposal, beer making and in cooking oil used to prepare potato chips.
(iv) As a lubricant in the gearboxes.