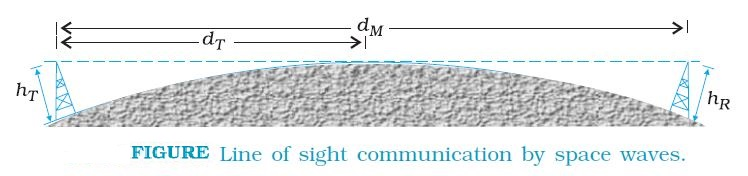
Sky Wave Propagation
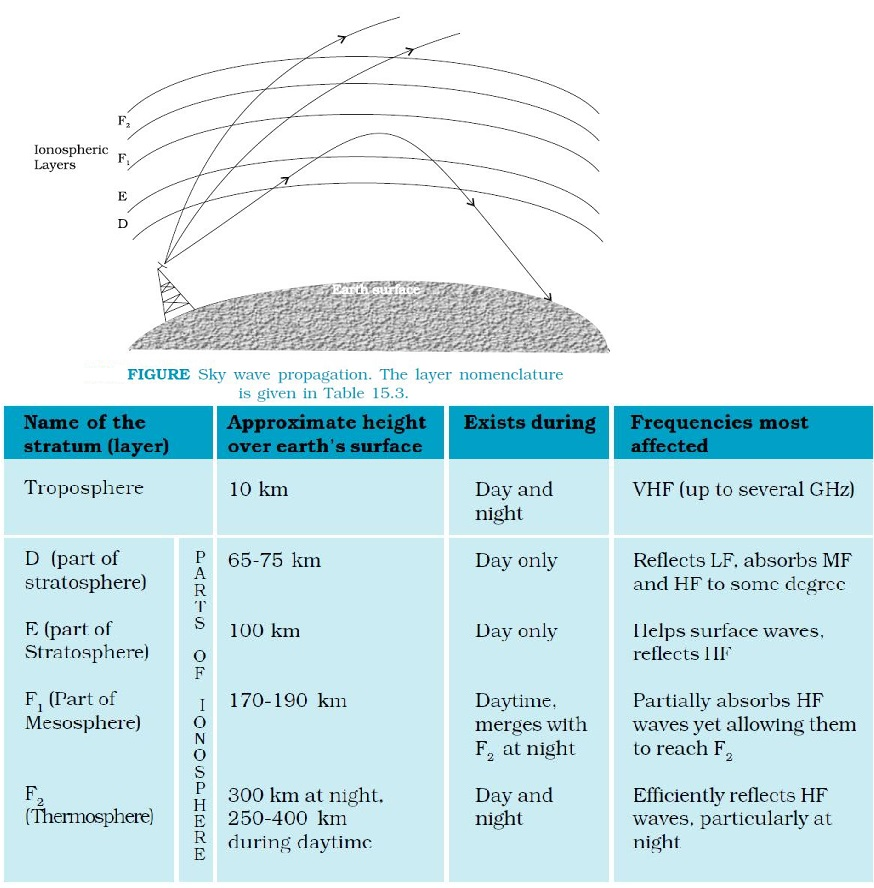
In the frequency range from a few MHz up to 30 to 40 MHz, long distance communication can be achieved by ionospheric reflection of radio waves back towards the earth. This mode of propagation is called sky wave propagation and is used by short wave broadcast services.
The ionosphere is so called because of the presence of a large number of ions or charged particles.
The ionosphere is further subdivided into several layers, the details of which are given in Table.
The degree of ionization varies with the height.
The density of atmosphere decreases with height.
The ionospheric layer acts as a reflector for a certain range of frequencies (3 to 30 MHz).
Electromagnetic waves of frequencies higher than 30 MHz penetrate the ionosphere and escape.
The phenomenon of bending of em waves so that they are diverted towards the earth is similar to total internal reflection in optics.
`text(Critical Frequency :)`
The highest frequency of radio wave that can be reflected back by the ionosphere is called critical frequency.
Critical frequency (`nu_c`) `=9(N_(max))^(1//2)`
Where, N = `text(number density of electrons)//text(metre)^3`.
`text(Skip Distance :)`
The minimum distance from the transmitter at which a sky wave of a frequency but not more than critical frequency, is sent back to the earth.
Skip distance (`D_(s k i p)`) `= 2h(nu_(max) // nu_c)^2 -1`
where h is height of reflecting layer of atmosphere, `V_(max)` is maximum frequency of electromagnetic waves and `V_c` is critical frequency.
`text(Fading :)`
The variation in the strength of a signal at receiver due to interference of waves, is called fading.
The ionosphere is so called because of the presence of a large number of ions or charged particles.
The ionosphere is further subdivided into several layers, the details of which are given in Table.
The degree of ionization varies with the height.
The density of atmosphere decreases with height.
The ionospheric layer acts as a reflector for a certain range of frequencies (3 to 30 MHz).
Electromagnetic waves of frequencies higher than 30 MHz penetrate the ionosphere and escape.
The phenomenon of bending of em waves so that they are diverted towards the earth is similar to total internal reflection in optics.
`text(Critical Frequency :)`
The highest frequency of radio wave that can be reflected back by the ionosphere is called critical frequency.
Critical frequency (`nu_c`) `=9(N_(max))^(1//2)`
Where, N = `text(number density of electrons)//text(metre)^3`.
`text(Skip Distance :)`
The minimum distance from the transmitter at which a sky wave of a frequency but not more than critical frequency, is sent back to the earth.
Skip distance (`D_(s k i p)`) `= 2h(nu_(max) // nu_c)^2 -1`
where h is height of reflecting layer of atmosphere, `V_(max)` is maximum frequency of electromagnetic waves and `V_c` is critical frequency.
`text(Fading :)`
The variation in the strength of a signal at receiver due to interference of waves, is called fading.