Kirchhoffs First Law of Capacitor
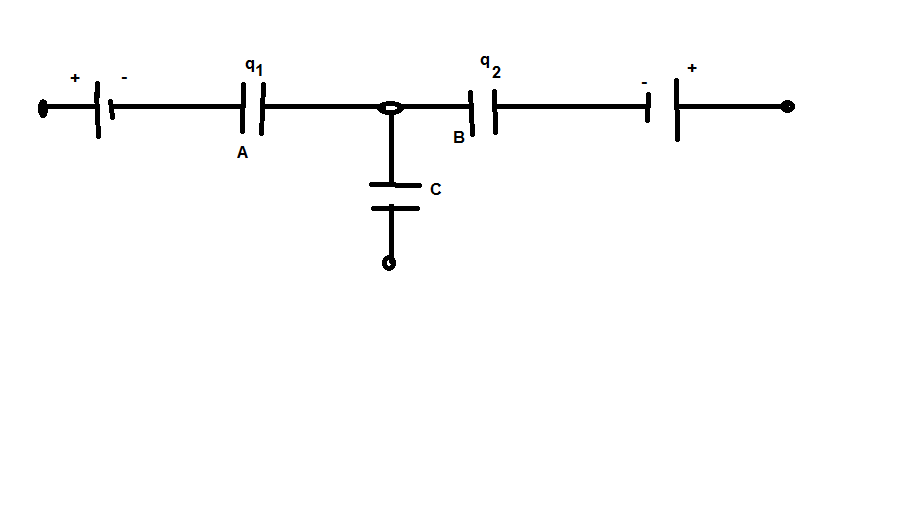
This law is based on the principle of conservation of charge .
i.e. at the junction `sum q = 0`
This law is useful in determining the nature of charge on an unknown capacitor plate.
As no charge can accumulate at the junction O, so if `x` is charge on plate 1 of C, then
from Fig `-q_1 + q_2 +x = 0`
`x = q_1 - q_2`
i.e. plate 1 has a charge `(q_1 - q_2)` and plate 2 has a charge `-(q_1 - q_2)`
i.e. at the junction `sum q = 0`
This law is useful in determining the nature of charge on an unknown capacitor plate.
As no charge can accumulate at the junction O, so if `x` is charge on plate 1 of C, then
from Fig `-q_1 + q_2 +x = 0`
`x = q_1 - q_2`
i.e. plate 1 has a charge `(q_1 - q_2)` and plate 2 has a charge `-(q_1 - q_2)`