Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
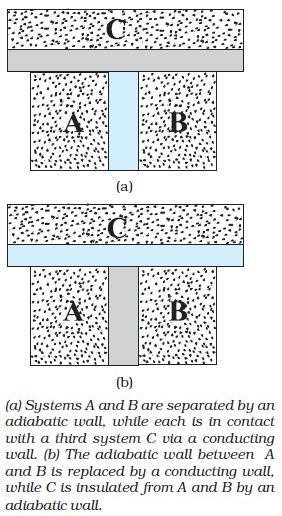
Imagine two systems A and B, separated by an adiabatic wall, while each is in contact with a third system C, via a conducting wall [Fig.(a)]. The states of the systems (i.e., their macroscopic variables) will change until both A and B come to thermal equilibrium with C. After this is achieved, suppose that the adiabatic wall between A and B is replaced by a conducting wall and C is insulated from A and B by an adiabatic wall [Fig.(b)]. It is found that the states of A and B change no further i.e. they are found to be in thermal equilibrium with each other.
The `text(Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics)`, which states that `text('two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system separately are in thermal equilibrium with each other')`.
If A and B are separately in equilibrium with C, `T_A = T_C` and `T_B = T_C`. This implies that `T_A = T_B` i.e. the systems A and B are also in thermal equilibrium.
The `text(Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics)`, which states that `text('two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system separately are in thermal equilibrium with each other')`.
If A and B are separately in equilibrium with C, `T_A = T_C` and `T_B = T_C`. This implies that `T_A = T_B` i.e. the systems A and B are also in thermal equilibrium.