Isothermal Process
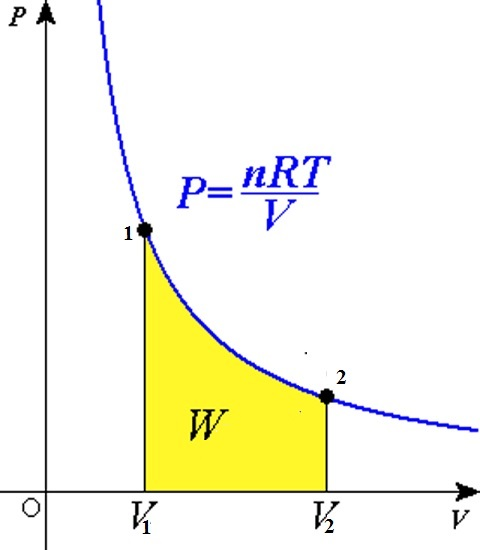
For an isothermal process (T fixed), the ideal gas equation gives
PV = constant
i.e., pressure of a given mass of gas varies inversely as its volume. This is nothing but Boyle's Law.
Suppose an ideal gas goes isothermally (at temperature T ) from its initial state (`P_1, V_1`) to the final state (`P_2, V_2`). At any intermediate stage with pressure P and volume change from V to V + ΔV (ΔV small)
`ΔW = P Δ V`
Taking (ΔV → 0) and summing the quantity ΔW over the entire process,
`W=int_(V_1)^(V_2)PdV`
`W=nRTint_(V_1)^(V_2)(dV)/V`
`W=nRTln((V_2)/(V_1))`
PV = constant
i.e., pressure of a given mass of gas varies inversely as its volume. This is nothing but Boyle's Law.
Suppose an ideal gas goes isothermally (at temperature T ) from its initial state (`P_1, V_1`) to the final state (`P_2, V_2`). At any intermediate stage with pressure P and volume change from V to V + ΔV (ΔV small)
`ΔW = P Δ V`
Taking (ΔV → 0) and summing the quantity ΔW over the entire process,
`W=int_(V_1)^(V_2)PdV`
`W=nRTint_(V_1)^(V_2)(dV)/V`
`W=nRTln((V_2)/(V_1))`