Inertial and Non-Inertial Frame of Reference
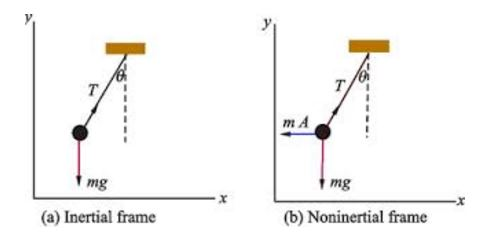
(a) Inertial Frame:-
A frame of reference either at rest or moving with a uniform velocity (zero acceleration) is known as inertial frame. All the laws of physics hold good in such a frame.
(b) Non-Inertial or Accelerated Frame:-
It is a frame of reference which is either having a uniform linear acceleration or is being rotated with uniform speed.
A frame of reference either at rest or moving with a uniform velocity (zero acceleration) is known as inertial frame. All the laws of physics hold good in such a frame.
(b) Non-Inertial or Accelerated Frame:-
It is a frame of reference which is either having a uniform linear acceleration or is being rotated with uniform speed.