Skeletal System
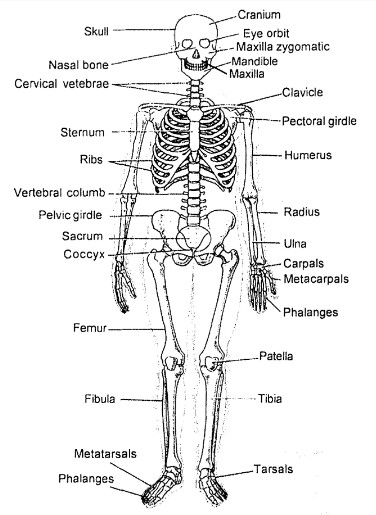
There are two main forms of skeleton :
(a) Exoskeleton
(b) Endoskeleton
Exoskeleton:- This is developed from epidermis.
Example Hairs, Nails, Claws, Hoofs, Horns and feathers, etc. Exoskeleton is ectodermal in origin & non living. Mesodermal exoskeleton occur in fishes scales, crocodiles, turtles. etc.
Endoskeleton :- It is present inside the body & mesodermal in origin. In vertebrate endoskeleton is formed of bone and cartilage. These are living in nature.
(a) Exoskeleton
(b) Endoskeleton
Exoskeleton:- This is developed from epidermis.
Example Hairs, Nails, Claws, Hoofs, Horns and feathers, etc. Exoskeleton is ectodermal in origin & non living. Mesodermal exoskeleton occur in fishes scales, crocodiles, turtles. etc.
Endoskeleton :- It is present inside the body & mesodermal in origin. In vertebrate endoskeleton is formed of bone and cartilage. These are living in nature.