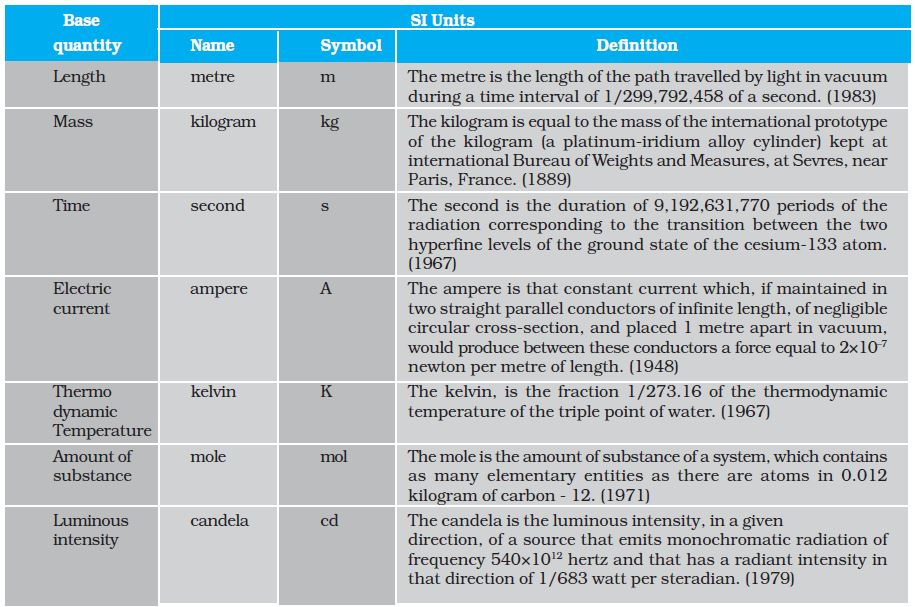
The International System of Units
In earlier time scientists of different countries were using different systems of units for measurement. Three such systems, the CGS, the FPS (or British) system and the MKS system were in use extensively till recently.
The base units for length, mass and time in these systems were as follows :
- In CGS system they were centimetre, gram and second respectively.
- In FPS system they were foot, pound and second respectively.
- In MKS system they were metre, kilogram and second respectively.
The system of units which is at present internationally accepted for measurement is the French for International System of Units, abbreviated as SI. The SI, with standard scheme of symbols, units and abbreviations, was developed and recommended by General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1971 for international usage in scientific, technical, industrial and commercial work. Because SI units used decimal system, conversions within the system are quite simple and convenient.
`text(Besides the seven base units, there are two more units :)`
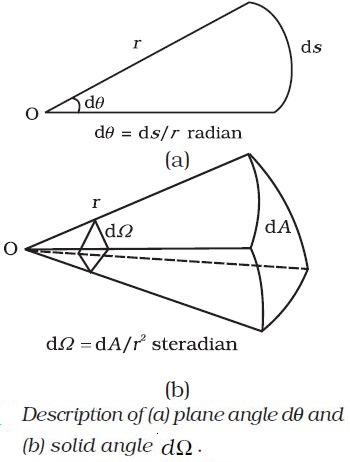
(a) Plane angle `dθ` as the ratio of length of arc `ds` to the radius `r`.
(b) Solid angle `dΩ` as the ratio of the intercepted area `dA` of the spherical surface, described about the apex O as the centre, to the square of its radius `r`, as shown in Fig.
The unit for plane angle is radian with the symbol rad and the unit for the solid angle is steradian with the symbol sr.
Both these are dimensionless quantities.
The base units for length, mass and time in these systems were as follows :
- In CGS system they were centimetre, gram and second respectively.
- In FPS system they were foot, pound and second respectively.
- In MKS system they were metre, kilogram and second respectively.
The system of units which is at present internationally accepted for measurement is the French for International System of Units, abbreviated as SI. The SI, with standard scheme of symbols, units and abbreviations, was developed and recommended by General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1971 for international usage in scientific, technical, industrial and commercial work. Because SI units used decimal system, conversions within the system are quite simple and convenient.
`text(Besides the seven base units, there are two more units :)`
(a) Plane angle `dθ` as the ratio of length of arc `ds` to the radius `r`.
(b) Solid angle `dΩ` as the ratio of the intercepted area `dA` of the spherical surface, described about the apex O as the centre, to the square of its radius `r`, as shown in Fig.
The unit for plane angle is radian with the symbol rad and the unit for the solid angle is steradian with the symbol sr.
Both these are dimensionless quantities.