Abnormal Molecular Masses :
Vapour pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression and osmotic pressure are colligative properties which depend upon the fraction of solute and solvent particles in solution and not upon the chemical nature of the solute. If solute molecules dissociates in solution, there are more particles in solution and therefore, lowering of vapour pressure shows an increased effect.
`NaCl_(s) ⇋ Na_(aq)^(+) + Cl_(aq)^(-)`
If the solute molecules associates in solution, there are less particles in solution, and therefore lowering of vapour pressure shows a decreased effect.
`nAB ⇋ (AB)_n`
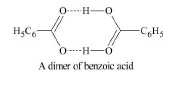
`2C_6H_5COOH ⇋ (C_6H_5COOH))_2`
`text(The molecular mass of a solute is inversely proportional to its molality)` : If colligative molality is `2m`, the calculated molecular mass is one-half of the actual molecular mass of the solute. If colligative molality is `3 m`, the calculated molecular mass is one third of the actual molecular mass of the solute. The molecular mass of benzoic acid is `122` `g//mol`. But the molecular mass of benzoic acid dissolved in benzene is found to be `244` `g//mol` by using a colligative property. Benzoic acid associates to form a dimer and therefore its colligative molality is one-half of the molality of benzoic acid. As molecular mass of a solute is inversely proportional to molality, the molecular mass of benzoic acid determined using a colligative property is double the actual molecular mass of benzoic acid. We can summarize the results as :
(i) `text(The extent of dissociation and colligative property)` : A solute dissociates completely or partially in solution makes available more particles than would otherwise be present in solution and therefore, a colligative property shows an increased effect. For example, molecular masses obtained of strong acids, bases and salts are much less than their normal values. As an example, one particle of potassium chloride on dissociation in water gives two particles, `K^(+)` and `Cl^(-)` and therefore, the molecular mass obtained by a colligative property is half of its normal molecular mass.
`K^(+) Cl_(s)^(-) + nH_2O -> K_(aq)^(+) + Cl_(aq)^(-)`
(ii) `text(The extent of association and colligative property)` : A solute that associates in solution provides less particles that would otherwise be present in solution and therefore, the colligative property shows the decreased effect. For example, benzoic acid in benzene is found to have molecular mass which is just twice its normal molecular mass. It is found that compounds which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds, e.g., phenols, carboxylic acids, alcohols: because of association show decreased effect of colligative property.
`NaCl_(s) ⇋ Na_(aq)^(+) + Cl_(aq)^(-)`
If the solute molecules associates in solution, there are less particles in solution, and therefore lowering of vapour pressure shows a decreased effect.
`nAB ⇋ (AB)_n`
`2C_6H_5COOH ⇋ (C_6H_5COOH))_2`
`text(The molecular mass of a solute is inversely proportional to its molality)` : If colligative molality is `2m`, the calculated molecular mass is one-half of the actual molecular mass of the solute. If colligative molality is `3 m`, the calculated molecular mass is one third of the actual molecular mass of the solute. The molecular mass of benzoic acid is `122` `g//mol`. But the molecular mass of benzoic acid dissolved in benzene is found to be `244` `g//mol` by using a colligative property. Benzoic acid associates to form a dimer and therefore its colligative molality is one-half of the molality of benzoic acid. As molecular mass of a solute is inversely proportional to molality, the molecular mass of benzoic acid determined using a colligative property is double the actual molecular mass of benzoic acid. We can summarize the results as :
(i) `text(The extent of dissociation and colligative property)` : A solute dissociates completely or partially in solution makes available more particles than would otherwise be present in solution and therefore, a colligative property shows an increased effect. For example, molecular masses obtained of strong acids, bases and salts are much less than their normal values. As an example, one particle of potassium chloride on dissociation in water gives two particles, `K^(+)` and `Cl^(-)` and therefore, the molecular mass obtained by a colligative property is half of its normal molecular mass.
`K^(+) Cl_(s)^(-) + nH_2O -> K_(aq)^(+) + Cl_(aq)^(-)`
(ii) `text(The extent of association and colligative property)` : A solute that associates in solution provides less particles that would otherwise be present in solution and therefore, the colligative property shows the decreased effect. For example, benzoic acid in benzene is found to have molecular mass which is just twice its normal molecular mass. It is found that compounds which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds, e.g., phenols, carboxylic acids, alcohols: because of association show decreased effect of colligative property.