Combinations of drugs
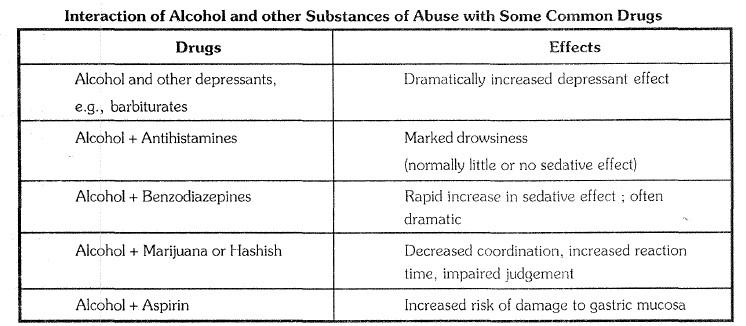
Some addicts use mixtures of drugs to have immediate 'kick' or 'charge'. Simultaneous use of drug (hemp derivatives, barbiturates, aspirin or antihistamines) and alcohol may produce dangerous effects, including death. When barbiturates and alcohol are taken together, each doubles the effect of the other. A mixture of cocaine and heroin, called speed ball, gives spontaneous kick of cocaine and prolonged pleasure of heroin.
The most common warning signs of drug and alcohol abuse among youth include drop in academic performance.
unexplained absence from school/college, lack of interest in personal hygiene, withdrawal, isolation, depression, fatigue, aggressive and rebellious behaviour, deteriorating relationships with family and friends. loss of interest in hobbies, change in sleeping and eating habits, fluctuations in weight, appetite, etc.
# There may even be some far-reaching implications of drug/alcohol abuse. If a abuser is unable to get money to buy drugs/alcohol he/she may turn to stealing. The adverse effects are just not restricted to the person who is using drugs or alcohol. At times, a drug/alcohol addict becomes the cause of mental and financial distress to his/her entire family and friends.
#Those who take drugs intravenously (direct injection into the vein using a needle and syringe), are much more
likely to acquire serious infections like AIDS and hepatitis B. The viruses, which are responsible for these diseases, are transferred from one person to another by sharing of infected needles and syringes. Both AIDS and Hepatitis B infections are chronic infections and ultimately fatal. AIDS can be transmitted to one's life partner through sexual contact while Hepatitis B is transmitted through infected blood.
#The use of alcohol during adolescence may also have long-term effects. It could lead to heavy drinking in adulthood. The chronic use of drugs and alcohol damages nervous system and liver (cirrhosis). The use of drugs and alcohol during pregnancy is also known to adversely affect the foetus.
# Another misuse of drugs is what certain sports-persons do to enhance their performance. They misuse narcotic analgesics, anabolic steroids, diuretics and certain hormones in sports to increase muscle strength and bulk and to promote aggressiveness and as a result increase athletic performance.
#The side-effects of the use of anabolic steroids in females include masculinisation (features like males), increased aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, abnormal menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth on the face and body, enlargement of clitoris, deepening of voice.
In males it includes acne, increased aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, reduction of size of the testicles, decreased sperm production, potential for kidney and liver dysfunction, breast enlargement, premature baldness, enlargement of the prostate gland. These effects may be permanent with prolonged use.
# In the adolescent male or female, severe facial and body acne, and premature closure of the growth
centres of the long bones may result in stunted growth.
The most common warning signs of drug and alcohol abuse among youth include drop in academic performance.
unexplained absence from school/college, lack of interest in personal hygiene, withdrawal, isolation, depression, fatigue, aggressive and rebellious behaviour, deteriorating relationships with family and friends. loss of interest in hobbies, change in sleeping and eating habits, fluctuations in weight, appetite, etc.
# There may even be some far-reaching implications of drug/alcohol abuse. If a abuser is unable to get money to buy drugs/alcohol he/she may turn to stealing. The adverse effects are just not restricted to the person who is using drugs or alcohol. At times, a drug/alcohol addict becomes the cause of mental and financial distress to his/her entire family and friends.
#Those who take drugs intravenously (direct injection into the vein using a needle and syringe), are much more
likely to acquire serious infections like AIDS and hepatitis B. The viruses, which are responsible for these diseases, are transferred from one person to another by sharing of infected needles and syringes. Both AIDS and Hepatitis B infections are chronic infections and ultimately fatal. AIDS can be transmitted to one's life partner through sexual contact while Hepatitis B is transmitted through infected blood.
#The use of alcohol during adolescence may also have long-term effects. It could lead to heavy drinking in adulthood. The chronic use of drugs and alcohol damages nervous system and liver (cirrhosis). The use of drugs and alcohol during pregnancy is also known to adversely affect the foetus.
# Another misuse of drugs is what certain sports-persons do to enhance their performance. They misuse narcotic analgesics, anabolic steroids, diuretics and certain hormones in sports to increase muscle strength and bulk and to promote aggressiveness and as a result increase athletic performance.
#The side-effects of the use of anabolic steroids in females include masculinisation (features like males), increased aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, abnormal menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth on the face and body, enlargement of clitoris, deepening of voice.
In males it includes acne, increased aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, reduction of size of the testicles, decreased sperm production, potential for kidney and liver dysfunction, breast enlargement, premature baldness, enlargement of the prostate gland. These effects may be permanent with prolonged use.
# In the adolescent male or female, severe facial and body acne, and premature closure of the growth
centres of the long bones may result in stunted growth.